A nuclear import inhibitory peptide ameliorates the severity of cholecystokinin-induced acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 15742402
- PMCID: PMC4250791
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i7.990
A nuclear import inhibitory peptide ameliorates the severity of cholecystokinin-induced acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Aim: To assess the effect of our novel cell-permeable nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) inhibitor peptide PN50 in an experimental model of acute pancreatitis. PN50 was produced by conjugating the cell-penetrating penetratin peptide with the nuclear localization signal of the NF-kappaB p50 subunit.
Methods: Pancreatitis was induced in male Wistar rats by administering 2X100 mug/kg body weight of cholecystokinin-octapeptide (CCK) intraperitoneally (IP) at an interval of 1 h. PN50-treated animals received 1 mg/kg of PN50 IP 30 min before or after the CCK injections. The animals were sacrificed 4 h after the first injection of CCK.
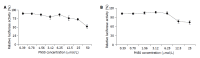
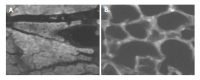
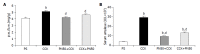
Results: All the examined laboratory (the pancreatic weight/body weight ratio, serum amylase activity, pancreatic levels of TNF-alpha and IL-6, degree of lipid peroxidation, reduced glutathione levels, NF-kappaB binding activity, pancreatic and lung myeloperoxidase activity) and morphological parameters of the disease were improved before and after treatment with the PN50 peptide. According to the histological findings, PN50 protected the animals against acute pancreatitis by favoring the induction of apoptotic, as opposed to necrotic acinar cell death associated with severe acute pancreatitis.
Conclusion: Our study implies that reversible inhibitors of stress-responsive transcription factors like NF-kappaB might be clinically useful for the suppression of the severity of acute pancreatitis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The anti-inflammatory effect of methylprednisolone occurs down-stream of nuclear factor-kappaB DNA binding in acute pancreatitis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Mar 19;464(2-3):217-27. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01380-3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12620516
-
Effects of bee venom on cholecystokinin octapeptide-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.Pancreas. 2008 Mar;36(2):e22-9. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31815a396b. Pancreas. 2008. PMID: 18376296
-
Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor ameliorates cholecystokinin-octapeptide-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Apr 28;13(16):2298-304. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i16.2298. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17511027 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB activation is detrimental in arginine-induced acute pancreatitis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2003 Mar 15;34(6):696-709. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(02)01373-4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003. PMID: 12633747
-
Beneficial effect of resveratrol on cholecystokinin-induced experimental pancreatitis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb 17;532(1-2):187-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.01.055. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16499907
Cited by
-
The neurotoxic effects of ampicillin-associated gut bacterial imbalances compared to those of orally administered propionic acid in the etiology of persistent autistic features in rat pups: effects of various dietary regimens.Gut Pathog. 2015 Mar 22;7:7. doi: 10.1186/s13099-015-0054-4. eCollection 2015. Gut Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25852770 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of oligonucleotide- and protein/peptide-based therapeutics in the management of toxicant/stressor-induced diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;397(3):1275-1310. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02683-3. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37688622 Review.
-
Inhibition of pancreatic oxidative damage by stilbene derivative dihydro-resveratrol: implication for treatment of acute pancreatitis.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 14;6:22859. doi: 10.1038/srep22859. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26971398 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory-Associated Bone Diseases.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;107:117-154. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28215222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Azithromycin Polarizes Macrophages to an M2 Phenotype via Inhibition of the STAT1 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.J Immunol. 2019 Aug 15;203(4):1021-1030. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801228. Epub 2019 Jul 1. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31263039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weber CK, Adler G. From acinar cell damage to systemic inflammatory response: current concepts in pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2001;1:356–362. - PubMed
-
- Makhija R, Kingsnorth AN. Cytokine storm in acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Gukovsky I, Gukovskaya AS, Blinman TA, Zaninovic V, Pandol SJ. Early NF-kappaB activation is associated with hormone-induced pancreatitis. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:G1402–G1414. - PubMed
-
- Han B, Logsdon CD. Cholecystokinin induction of mob-1 chemokine expression in pancreatic acinar cells requires NF-kappaB activation. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:C74–C82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

