Effect of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury on protein levels of leptin and orexin-A in peripheral blood and central secretory tissues
- PMID: 15742403
- PMCID: PMC4250760
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i7.1000
Effect of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury on protein levels of leptin and orexin-A in peripheral blood and central secretory tissues
Abstract
Aim: To explore the effect of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury on protein levels of leptin and orexin-A in peripheral blood and their central secretory tissues and to find out the role leptin and orexin-A play in acute inflammatory responses.
Methods: An intestinal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury model of rats was established and rats were divided randomly into six groups: sham-operation group, 60 min ischemia/30 min reperfusion group (I60'R30'), I60'R90', I60'R150', I60'R240' and I60'R360', 9 rats each group. Two highly-sensitive radioimmunoassays for leptin and orexin-A were established and used to check the change of their concentrations in peripheral blood and central secretory tissues before and after intestinal I/R injury.
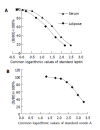
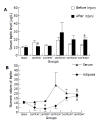
Results: Compared with the serum leptin level before injury, it decreased significantly in I60'R30' group and increased significantly in I60'R360' group; compared to sham-operation group after injury, serum leptin level increased significantly in I60'R360' group; compared to sham-operation group after injury, adipose leptin levels decreased significantly in I60'R30' and I60'R90' groups, while increased significantly in I60'R360' group. There was no significant difference between the expression levels of orexin-A before and after I/R injury.
Conclusion: Leptin has a time-dependent response and orexin-A has a delayed response to acute inflammatory stimuli such as intestinal I/R injury and they may participate in metabolic disorders in injury as inflammatory cytokines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous leptin fluctuates in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury and represents a potential therapeutic target.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 21;16(43):5424-34. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5424. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21086559 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury on leptin and orexin-A levels].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jun;26(6):719-24. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16793584 Chinese.
-
Effect of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury on leptin and orexin-A levels.Front Med China. 2007 Feb;1(1):87-92. doi: 10.1007/s11684-007-0017-3. Front Med China. 2007. PMID: 24557624
-
[Effect of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury on protein and mRNA levels of orexin-A].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006 Jul;37(4):574-7. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006. PMID: 16909605 Chinese.
-
[Primary research of the effect of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury on Leptin concentrations].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2003 Dec;15(12):722-5. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2003. PMID: 14659053 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The effect of leptin on intestinal recovery following ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat.Pediatr Surg Int. 2007 May;23(5):473-8. doi: 10.1007/s00383-006-1863-9. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007. PMID: 17203324
-
Endogenous leptin fluctuates in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury and represents a potential therapeutic target.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 21;16(43):5424-34. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i43.5424. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21086559 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of leptin against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat small intestine.BMC Gastroenterol. 2005 Nov 21;5:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-5-37. BMC Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16300680 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the link between leptin, ghrelin and different types of colitis.Ann Gastroenterol. 2011;24(1):20-28. Ann Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 24714276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Imagawa K, Numata Y, Katsuura G, Sakaguchi I, Morita A, Kikuoka S, Matumoto Y, Tsuji T, Tamaki M, Sasakura K, et al. Structure-function studies of human leptin. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:35245–35249. - PubMed
-
- Fantuzzi G, Faggioni R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;68:437–446. - PubMed
-
- Hausberg M, Morgan DA, Mitchell JL, Sivitz WI, Mark AL, Haynes WG. Leptin potentiates thermogenic sympathetic responses to hypothermia: a receptor-mediated effect. Diabetes. 2002;51:2434–2440. - PubMed
-
- Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, Klein AS, Bulkley GB, Bao C, Noble PW, et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. 1998;12:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Martí A, Berraondo B, Martínez JA. Leptin: physiological actions. J Physiol Biochem. 1999;55:43–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources