Phenotypic and functional characterisation of CCR7+ and CCR7- CD4+ memory T cells homing to the joints in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- PMID: 15743472
- PMCID: PMC1065323
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1485
Phenotypic and functional characterisation of CCR7+ and CCR7- CD4+ memory T cells homing to the joints in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Abstract
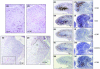
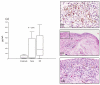
The aim of the study was to characterise CCR7+ and CCR7- memory T cells infiltrating the inflamed joints of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and to investigate the functional and anatomical heterogeneity of these cell subsets in relation to the expression of the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR5. Memory T cells freshly isolated from the peripheral blood and synovial fluid (SF) of 25 patients with JIA were tested for the expression of CCR7, CCR5, CXCR3 and interferon-gamma by flow cytometry. The chemotactic activity of CD4 SF memory T cells from eight patients with JIA to inflammatory (CXCL11 and CCL3) and homeostatic (CCL19, CCL21) chemokines was also evaluated. Paired serum and SF samples from 28 patients with JIA were tested for CCL21 concentrations. CCR7, CXCR3, CCR5 and CCL21 expression in synovial tissue from six patients with JIA was investigated by immunohistochemistry. Enrichment of CD4+, CCR7- memory T cells was demonstrated in SF in comparison with paired blood from patients with JIA. SF CD4+CCR7- memory T cells were enriched for CCR5+ and interferon-gamma+ cells, whereas CD4+CCR7+ memory T cells showed higher coexpression of CXCR3. Expression of CCL21 was detected in both SF and synovial membranes. SF CD4+ memory T cells displayed significant migration to both inflammatory and homeostatic chemokines. CCR7+ T cells were detected in the synovial tissue in either diffuse perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates or organised lymphoid aggregates. In synovial tissue, a large fraction of CCR7+ cells co-localised with CXCR3, especially inside lymphoid aggregates, whereas CCR5+ cells were enriched in the sublining of the superficial subintima. In conclusion, CCR7 may have a role in the synovial recruitment of memory T cells in JIA, irrespective of the pattern of lymphoid organisation. Moreover, discrete patterns of chemokine receptor expression are detected in the synovial tissue.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemokine and chemokine receptor analysis reveals elevated interferon-inducible protein-10 (IP)-10/CXCL10 levels and increased number of CCR5+ and CXCR3+ CD4 T cells in synovial fluid of patients with enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA).Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Jun;148(3):515-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03377.x. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17374135 Free PMC article.
-
Selective recruitment of polarized T cells expressing CCR5 and CXCR3 to the inflamed joints of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Apr;43(4):765-74. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<765::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-B. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 10765921
-
Cytokine flexibility of early and differentiated memory T helper cells in juvenile idiopathic arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2004 Oct;31(10):2048-54. J Rheumatol. 2004. PMID: 15468374
-
Chemokine-mediated control of T cell traffic in lymphoid and peripheral tissues.Mol Immunol. 2005 May;42(7):799-809. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.06.040. Epub 2004 Nov 23. Mol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15829268 Review.
-
[Chemokines and chemokine receptors in multiple sclerosis].Nihon Rinsho. 2003 Aug;61(8):1422-7. Nihon Rinsho. 2003. PMID: 12962033 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Chemokine and chemokine receptor analysis reveals elevated interferon-inducible protein-10 (IP)-10/CXCL10 levels and increased number of CCR5+ and CXCR3+ CD4 T cells in synovial fluid of patients with enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA).Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Jun;148(3):515-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03377.x. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17374135 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomics of blood reveals a natural killer cell subset depletion in tuberculosis.EBioMedicine. 2020 Mar;53:102686. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102686. Epub 2020 Feb 27. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32114394 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor mRNA-transfected dendritic cells stimulate the generation of CTL that recognize neuroblastoma-associated antigens and kill tumor cells: immunotherapeutic implications.Neoplasia. 2006 Oct;8(10):833-42. doi: 10.1593/neo.06415. Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 17032500 Free PMC article.
-
APL-2, an altered peptide ligand derived from heat-shock protein 60, induces interleukin-10 in peripheral blood mononuclear cell derived from juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients and downregulates the inflammatory response in collagen-induced arthritis model.Clin Exp Med. 2015 Feb;15(1):31-9. doi: 10.1007/s10238-014-0273-x. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 24474501
-
[Concepts on the pathogenesis of juvenile idiopathic arthritis].Z Rheumatol. 2008 Mar;67(2):111-6, 118-20. doi: 10.1007/s00393-008-0276-7. Z Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18309499 Review. German.
References
-
- Harris ED., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1277–1289. - PubMed
-
- Iannone F, Corrigall VM, Kingsley GH, Panayi GS. Evidence for the continuous recruitment and activation of T cells into the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:2706–2713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

