Balance between survivin, a key member of the apoptosis inhibitor family, and its specific antibodies determines erosivity in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15743483
- PMCID: PMC1065333
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1498
Balance between survivin, a key member of the apoptosis inhibitor family, and its specific antibodies determines erosivity in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
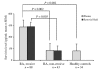
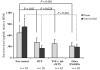
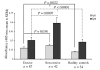
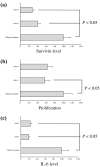
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a highly heterogeneous disease with respect to its joint destructivity. The reasons underlying this heterogeneity are unknown. Deficient apoptosis in rheumatoid synovial tissue has been recently demonstrated. We have therefore decided to study the synovial expression of survivin, a key member of the apoptosis inhibitor family. The levels of survivin and antibodies against survivin were assessed by an ELISA in matched blood and synovial fluid samples collected from 131 RA patients. Results were related to joint erosivity at the time of sampling. Monocytes were transfected with survivin anti-sense oligonucleotides and were assessed for their ability to produce inflammatory cytokines. Survivin levels were significantly higher in patients with destructive disease as compared with in RA patients displaying a non-erosive disease. High survivin levels were an independent prognostic parameter for erosive RA. In contrast, high levels of antibodies against survivin were found in patients with non-erosive RA, and were negatively related to erosivity. Survivin levels in RA patients were influenced by treatment, being significantly lower among patients treated with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Specific suppression of survivin mRNA resulted in downregulation of IL-6 production. We conclude that survivin determines the erosive course of RA, whereas survivin antibodies lead to a less aggressive course of the disease. These findings together with decreased survivin levels upon disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug treatment, and the downregulation of inflammatory response using survivin anti-sense oligonucleotides, suggest that extracellular survivin expression mediates the erosive course of joint disease whereas autoimmune responses to the same molecule, manifested as survivin targeting antibodies, mediate protection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synovial fluid expression of autoantibodies specific for RAGE relates to less erosive course of rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Aug;46(8):1367-71. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem141. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17569744
-
Anti-Fc gamma receptor III autoantibody is associated with soluble receptor in rheumatoid arthritis serum and synovial fluid.J Autoimmun. 1995 Apr;8(2):249-65. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1995.0019. J Autoimmun. 1995. PMID: 7612151
-
Decreased levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products in patients with rheumatoid arthritis indicating deficient inflammatory control.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):R817-24. doi: 10.1186/ar1749. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15987483 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological survivin expression links viral infections with pathogenesis of erosive rheumatoid arthritis.Scand J Immunol. 2007 Aug-Sep;66(2-3):192-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2007.01977.x. Scand J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17635796 Review.
-
Anti-CCP Antibody, a Marker for the Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Nov;1143:268-85. doi: 10.1196/annals.1443.013. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 19076355 Review.
Cited by
-
The Presence of Survivin on B Cells from Myasthenia Gravis Patients and the Potential of an Antibody to a Modified Survivin Peptide to Alleviate Weakness in an Animal Model.J Immunol. 2020 Oct 1;205(7):1743-1751. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000482. Epub 2020 Aug 24. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32839239 Free PMC article.
-
The proto-oncogene survivin splice variant 2B is induced by PDGF and leads to cell proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Sci Rep. 2015 May 22;5:9795. doi: 10.1038/srep09795. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25997820 Free PMC article.
-
Yin Yang 1 (YY1): Regulation of Survivin and Its Role In Invasion and Metastasis.Crit Rev Oncog. 2017;22(1-2):23-36. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2017020836. Crit Rev Oncog. 2017. PMID: 29604934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular apoptotic pathways: a potential target for reducing joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflamm Res. 2018 Mar;67(3):219-231. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1116-5. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29164267 Review.
-
A list of candidate cancer biomarkers for targeted proteomics.Biomark Insights. 2007 Feb 7;1:1-48. Biomark Insights. 2007. PMID: 19690635 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

