Combined global localization analysis and transcriptome data identify genes that are directly coregulated by Adr1 and Cat8
- PMID: 15743812
- PMCID: PMC1061606
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2138-2146.2005
Combined global localization analysis and transcriptome data identify genes that are directly coregulated by Adr1 and Cat8
Abstract
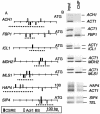
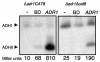
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, glucose depletion causes a profound alteration in metabolism, mediated in part by global transcriptional changes. Many of the transcription factors that regulate these changes act combinatorially. We have analyzed combinatorial regulation by Adr1 and Cat8, two transcription factors that act during glucose depletion, by combining genome-wide expression and genome-wide binding data. We identified 32 genes that are directly activated by Adr1, 28 genes that are directly activated by Cat8, and 14 genes that are directly regulated by both. Our analysis also uncovered promoters that Adr1 binds but does not regulate and promoters that are indirectly regulated by Cat8, stressing the advantage of combining global expression and global localization analysis to find directly regulated targets. At most of the coregulated promoters, the in vivo binding of one factor is independent of the other, but Adr1 is required for optimal Cat8 binding at two promoters with a poor match to the Cat8 binding consensus. In addition, Cat8 is required for Adr1 binding at promoters where Adr1 is not required for transcription. These data provide a comprehensive analysis of the direct, indirect, and combinatorial requirements for these two global transcription factors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adr1 and Cat8 mediate coactivator recruitment and chromatin remodeling at glucose-regulated genes.PLoS One. 2008 Jan 16;3(1):e1436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001436. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18197247 Free PMC article.
-
14-3-3 (Bmh) proteins regulate combinatorial transcription following RNA polymerase II recruitment by binding at Adr1-dependent promoters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;33(4):712-24. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01226-12. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23207903 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple pathways are co-regulated by the protein kinase Snf1 and the transcription factors Adr1 and Cat8.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 11;278(28):26146-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301981200. Epub 2003 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12676948
-
Transcriptional regulation of nonfermentable carbon utilization in budding yeast.FEMS Yeast Res. 2010 Feb;10(1):2-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2009.00555.x. Epub 2009 Jul 18. FEMS Yeast Res. 2010. PMID: 19686338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bursting into the nucleus.Sci Signal. 2008 Dec 23;1(51):pe54. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.151pe54. Sci Signal. 2008. PMID: 19109237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gains and Losses of Transcription Factor Binding Sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces paradoxus.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Jul 27;7(8):2245-57. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv138. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26220934 Free PMC article.
-
Pichia pastoris regulates its gene-specific response to different carbon sources at the transcriptional, rather than the translational, level.BMC Genomics. 2015 Mar 11;16(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1393-8. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25887254 Free PMC article.
-
Rewiring regulation on respiro-fermentative metabolism relieved Crabtree effects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 15;7(4):1034-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.06.004. eCollection 2022 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35801089 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae acetyltransferase Gcn5 exerts antagonistic pleiotropic effects on chronological ageing.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Oct 23;15(20):10915-10937. doi: 10.18632/aging.205109. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37874684 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based transcriptome engineering promotes a fermentative transcriptional state in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):E7428-E7437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603577113. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27810962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bojunga, N., and K. D. Entian. 1999. Cat8p, the activator of gluconeogenic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, regulates carbon source-dependent expression of NADP-dependent cytosolic isocitrate dehydrogenase (Idp2p) and lactate permease (Jen1p). Mol. Gen. Genet. 262:869-875. - PubMed
-
- Bojunga, N., P. Kotter, and K. D. Entian. 1998. The succinate/fumarate transporter Acr1p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is part of the gluconeogenic pathway and its expression is regulated by Cat8p. Mol. Gen. Genet. 260:453-461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
