Novel checkpoint response to genotoxic stress mediated by nucleolin-replication protein a complex formation
- PMID: 15743838
- PMCID: PMC1061594
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2463-2474.2005
Novel checkpoint response to genotoxic stress mediated by nucleolin-replication protein a complex formation
Abstract
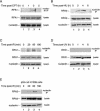
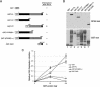
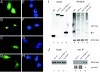
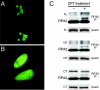
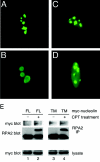
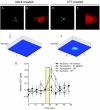
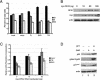
Human replication protein A (RPA), the primary single-stranded DNA-binding protein, was previously found to be inhibited after heat shock by complex formation with nucleolin. Here we show that nucleolin-RPA complex formation is stimulated after genotoxic stresses such as treatment with camptothecin or exposure to ionizing radiation. Complex formation in vitro and in vivo requires a 63-residue glycine-arginine-rich (GAR) domain located at the extreme C terminus of nucleolin, with this domain sufficient to inhibit DNA replication in vitro. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies demonstrate that the nucleolin-RPA interaction after stress occurs both in the nucleoplasm and in the nucleolus. Expression of the GAR domain or a nucleolin mutant (TM) with a constitutive interaction with RPA is sufficient to inhibit entry into S phase. Increasing cellular RPA levels by overexpression of the RPA2 subunit minimizes the inhibitory effects of nucleolin GAR or TM expression on chromosomal DNA replication. The arrest is independent of p53 activation by ATM or ATR and does not involve heightened expression of p21. Our data reveal a novel cellular mechanism that represses genomic replication in response to genotoxic stress by inhibition of an essential DNA replication factor.
Figures
References
-
- Araujo, S. J., and R. D. Wood. 1999. Protein complexes in nucleotide excision repair. Mutat. Res. 435:23-33. - PubMed
-
- Bembenek, J., and H. Yu. 2003. Regulation of CDC14: pathways and checkpoints of mitotic exit. Front. Biosci. 8:d1275-d1287. - PubMed
-
- Biamonti, G., and S. Riva. 1994. New insights into the auxiliary domains of eukaryotic RNA binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 340:1-8. - PubMed
-
- Bivona, T. G., I. Perez De Castro, I. M. Ahearn, T. M. Grana, V. K. Chiu, P. J. Lockyer, P. J. Cullen, A. Pellicer, A. D. Cox, and M. R. Philips. 2003. Phospholipase Cγ activates Ras on the Golgi apparatus by means of RasGRP1. Nature 424:694-698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
