Human Fas-associated factor 1, interacting with ubiquitinated proteins and valosin-containing protein, is involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway
- PMID: 15743842
- PMCID: PMC1061599
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2511-2524.2005
Human Fas-associated factor 1, interacting with ubiquitinated proteins and valosin-containing protein, is involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway
Abstract
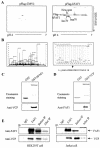
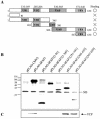
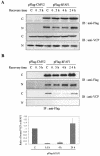
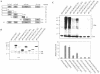
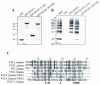
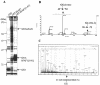
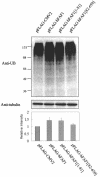
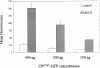
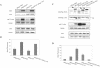
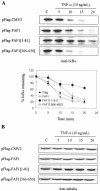
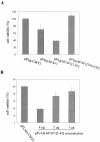
Human Fas-associated factor 1 (hFAF1) is a novel protein having multiubiquitin-related domains. We investigated the cellular functions of hFAF1 and found that valosin-containing protein (VCP), the multiubiquitin chain-targeting factor in the degradation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, is a binding partner of hFAF1. hFAF1 is associated with the ubiquitinated proteins via the newly identified N-terminal UBA domain and with VCP via the C-terminal UBX domain. The overexpression of hFAF1 and a truncated UBA domain inhibited the degradation of ubiquitinated proteins and increased cell death. These results suggest that hFAF1 binding to ubiquitinated protein and VCP is involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. We hypothesize that hFAF1 may serve as a scaffolding protein that regulates protein degradation in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complex of Fas-associated factor 1 (FAF1) with valosin-containing protein (VCP)-Npl4-Ufd1 and polyubiquitinated proteins promotes endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD).J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):6998-7011. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417576. Epub 2013 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23293021 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain in human Fas associated factor 1 inhibits tumor formation by promoting Hsp70 degradation.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e40361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040361. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22876279 Free PMC article.
-
Valosin-containing protein is a multi-ubiquitin chain-targeting factor required in ubiquitin-proteasome degradation.Nat Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;3(8):740-4. doi: 10.1038/35087056. Nat Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11483959
-
Delivery of ubiquitinated substrates to protein-unfolding machines.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;7(8):742-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb0805-742. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16056265 Review.
-
Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe?Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:50-69. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24157661 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome-wide association study and eQTL analysis to assess the genetic basis of bulb-yield traits in garlic (Allium sativum).BMC Genomics. 2019 Aug 17;20(1):657. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6025-2. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31419936 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the catalytic D2 domain of the AAA+ ATPase p97 reveals a putative helical split-washer-type mechanism for substrate unfolding.FEBS Lett. 2020 Mar;594(5):933-943. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13667. Epub 2019 Nov 22. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 31701538 Free PMC article.
-
Why do cellular proteins linked to K63-polyubiquitin chains not associate with proteasomes?EMBO J. 2013 Feb 20;32(4):552-65. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.354. Epub 2013 Jan 11. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23314748 Free PMC article.
-
Complex of Fas-associated factor 1 (FAF1) with valosin-containing protein (VCP)-Npl4-Ufd1 and polyubiquitinated proteins promotes endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD).J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):6998-7011. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417576. Epub 2013 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23293021 Free PMC article.
-
Neurorestorative Effects of a Novel Fas-Associated Factor 1 Inhibitor in the MPTP Model: An [18F]FE-PE2I Positron Emission Tomography Analysis Study.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 25;11:953. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00953. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32676027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bays, N. W., and R. Y. Hampton. 2002. Cdc48-ufd1-npl4: stuck in the middle with Ub. Curr. Biol. 12:R366-R371. - PubMed
-
- Becker, K., P. Schneider, K. Hofmann, C. Mattmann, and J. Tschopp. 1997. Interaction of Fas(Apo-1/CD95) with proteins implicated in the ubiquitination pathway. FEBS Lett. 412:102-106. - PubMed
-
- Buchberger, A., M. J. Howard, M. Proctor, and M. Bycroft. 2001. The UBX domain: a widespread ubiquitin-like module. J. Mol. Biol. 307:17-24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
