Neurabin/protein phosphatase-1 complex regulates dendritic spine morphogenesis and maturation
- PMID: 15743906
- PMCID: PMC1087240
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1054
Neurabin/protein phosphatase-1 complex regulates dendritic spine morphogenesis and maturation
Abstract
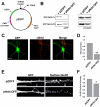
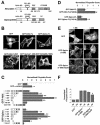
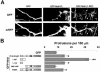
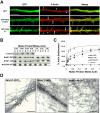
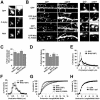
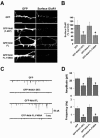
The majority of excitatory synapses in the mammalian brain form on filopodia and spines, actin-rich membrane protrusions present on neuronal dendrites. The biochemical events that induce filopodia and remodel these structures into dendritic spines remain poorly understood. Here, we show that the neuronal actin- and protein phosphatase-1-binding protein, neurabin-I, promotes filopodia in neurons and nonneuronal cells. Neurabin-I actin-binding domain bundled F-actin, promoted filopodia, and delayed the maturation of dendritic spines in cultured hippocampal neurons. In contrast, dimerization of neurabin-I via C-terminal coiled-coil domains and association of protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) with neurabin-I through a canonical KIXF motif inhibited filopodia. Furthermore, the expression of a neurabin-I polypeptide unable to bind PP1 delayed the maturation of neuronal filopodia into spines, reduced the synaptic targeting of AMPA-type glutamate (GluR1) receptors, and decreased AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Reduction of endogenous neurabin levels by interference RNA (RNAi)-mediated knockdown also inhibited the surface expression of GluR1 receptors. Together, our studies suggested that disrupting the functions of a cytoskeletal neurabin/PP1 complex enhanced filopodia and impaired surface GluR1 expression in hippocampal neurons, thereby hindering the morphological and functional maturation of dendritic spines.
Figures
References
-
- Barnes, A. P., Smith, F. D., 3rd, VanDongen, H. M., VanDongen, A. M., and Milgram, S. L. (2004). The identification of a second actin-binding region in spinophilin/neurabin II. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 124, 105–113. - PubMed
-
- Beattie, E. C., Carroll, R. C., Yu, X., Morishita, W., Yasuda, H., von Zastrow, M., and Malenka, R. C. (2000). Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1291–1300. - PubMed
-
- Bonhoeffer, T., and Yuste, R. (2002). Spine motility. Phenomenology, mechanisms, and function. Neuron 35, 1019–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

