FXYD3 (Mat-8), a new regulator of Na,K-ATPase
- PMID: 15743908
- PMCID: PMC1087241
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0878
FXYD3 (Mat-8), a new regulator of Na,K-ATPase
Abstract
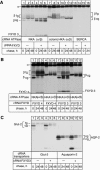
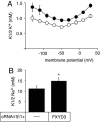
Four of the seven members of the FXYD protein family have been identified as specific regulators of Na,K-ATPase. In this study, we show that FXYD3, also known as Mat-8, is able to associate with and to modify the transport properties of Na,K-ATPase. In addition to this shared function, FXYD3 displays some uncommon characteristics. First, in contrast to other FXYD proteins, which were shown to be type I membrane proteins, FXYD3 may have a second transmembrane-like domain because of the presence of a noncleavable signal peptide. Second, FXYD3 can associate with Na,K- as well as H,K-ATPases when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. However, in situ (stomach), FXYD3 is associated only with Na,K-ATPase because its expression is restricted to mucous cells in which H,K-ATPase is absent. Coexpressed in Xenopus oocytes, FXYD3 modulates the glycosylation processing of the beta subunit of X,K-ATPase dependent on the presence of the signal peptide. Finally, FXYD3 decreases both the apparent affinity for Na+ and K+ of Na,K-ATPase.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and functional properties of two human FXYD3 (Mat-8) isoforms.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 22;281(51):39142-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605221200. Epub 2006 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17077088
-
Unusual degradation of alpha-beta complexes in Xenopus oocytes by beta-subunits of Xenopus gastric H-K-ATPase.Am J Physiol. 1998 Jul;275(1):C139-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.1.C139. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9688844
-
Intersubunit interactions in human X,K-ATPases: role of membrane domains M9 and M10 in the assembly process and association efficiency of human, nongastric H,K-ATPase alpha subunits (ATP1al1) with known beta subunits.Biochemistry. 2000 Oct 17;39(41):12688-98. doi: 10.1021/bi0009791. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 11027149
-
[FXYD proteins: novel regulators of Na,K-ATPase].Med Sci (Paris). 2006 Jun-Jul;22(6-7):633-8. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20062267633. Med Sci (Paris). 2006. PMID: 16828040 Review. French.
-
FXYD proteins: new regulators of Na-K-ATPase.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F241-50. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00126.2005. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16403837 Review.
Cited by
-
FXYD3 functionally demarcates an ancestral breast cancer stem cell subpopulation with features of drug-tolerant persisters.J Clin Invest. 2023 Nov 15;133(22):e166666. doi: 10.1172/JCI166666. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37966117 Free PMC article.
-
FXYD2 and Na,K-ATPase expression in isolated human proximal tubular cells: disturbed upregulation on renal hypomagnesemia?J Membr Biol. 2009 Oct;231(2-3):117-24. doi: 10.1007/s00232-009-9210-4. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Membr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19865785 Free PMC article.
-
FXYD8, a Novel Regulator of Renal Na+/K+-ATPase in the Euryhaline Teleost, Tetraodon nigroviridis.Front Physiol. 2017 Aug 8;8:576. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00576. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28848450 Free PMC article.
-
An atlas of human proximal epididymis reveals cell-specific functions and distinct roles for CFTR.Life Sci Alliance. 2020 Aug 27;3(11):e202000744. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000744. Print 2020 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2020. PMID: 32855272 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and tamoxifen up-regulate FXYD3 on breast cancer cells: assessing the differential roles of ER α and ZEB1.Springerplus. 2015 Jun 6;4:245. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1022-7. eCollection 2015. Springerplus. 2015. PMID: 26090296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arystarkhova, E., Wetzel, R. K., Asinovski, N. K., and Sweadner, K. J. (1999). The γ subunit modulates Na+ and K+ affinity of the renal Na,K-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33183–33185. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J. D., Nielsen, H., von Heijne, G., and Brunak, S. (2004). Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340, 783–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

