The Rok protein of Bacillus subtilis represses genes for cell surface and extracellular functions
- PMID: 15743949
- PMCID: PMC1064057
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.6.2010-2019.2005
The Rok protein of Bacillus subtilis represses genes for cell surface and extracellular functions
Abstract
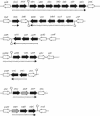
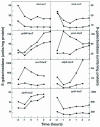
Rok is a repressor of the transcriptional activator ComK and is therefore an important regulator of competence in Bacillus subtilis (T. T. Hoa, P. Tortosa, M. Albano, and D. Dubnau, Mol. Microbiol. 43:15-26, 2002). To address the wider role of Rok in the physiology of B. subtilis, we have used a combination of transcriptional profiling, gel shift experiments, and the analysis of lacZ fusions. We demonstrate that Rok is a repressor of a family of genes that specify membrane-localized and secreted proteins, including a number of genes that encode products with antibiotic activity. We present evidence for the recent introduction of rok into the B. subtilis-Bacillus licheniformis-Bacilllus amyloliquefaciens group by horizontal transmission.
Figures


References
-
- Ash, C., J. A. E. Farrow, S. Walbanks, and M. D. Collins. 1991. Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the genus Bacillus revealed by comparative analysis of small-subunit-ribosomal RNA sequences. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 13:202-206.
-
- Bailey, T. L., and W. S. Noble. 2003. Searching for statistically significant regulatory modules. Bioinformatics 19(Suppl. 2):II16-II25. - PubMed
-
- Baldi, P., and G. W. Hatfield. 2002. DNA microarrays and gene expression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
-
- Berka, R. M., J. Hahn, M. Albano, I. Draskovic, M. Persuh, X. Cui, A. Sloma, W. Widner, and D. Dubnau. 2002. Microarray analysis of the Bacillus subtilis K-state: genome-wide expression changes dependent on ComK. Mol. Microbiol. 43:1331-1345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

