Repression of the pyr operon in Lactobacillus plantarum prevents its ability to grow at low carbon dioxide levels
- PMID: 15743958
- PMCID: PMC1064029
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.6.2093-2104.2005
Repression of the pyr operon in Lactobacillus plantarum prevents its ability to grow at low carbon dioxide levels
Abstract
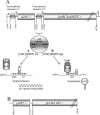
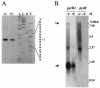
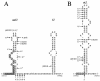
Carbamoyl phosphate is a precursor for both arginine and pyrimidine biosynthesis. In Lactobacillus plantarum, carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized from glutamine, ATP, and carbon dioxide by two sets of identified genes encoding carbamoyl phosphate synthase (CPS). The expression of the carAB operon (encoding CPS-A) responds to arginine availability, whereas pyrAaAb (encoding CPS-P) is part of the pyrR1BCAaAbDFE operon coding for the de novo pyrimidine pathway repressed by exogenous uracil. The pyr operon is regulated by transcription attenuation mediated by a trans-acting repressor that binds to the pyr mRNA attenuation site in response to intracellular UMP/phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate pools. Intracellular pyrimidine triphosphate nucleoside pools were lower in mutant FB335 (carAB deletion) harboring only CPS-P than in the wild-type strain harboring both CPS-A and CPS-P. Thus, CPS-P activity is the limiting step in pyrimidine synthesis. FB335 is unable to grow in the presence of uracil due to a lack of sufficient carbamoyl phosphate required for arginine biosynthesis. Forty independent spontaneous FB335-derived mutants that have lost regulation of the pyr operon were readily obtained by their ability to grow in the presence of uracil and absence of arginine; 26 harbored mutations in the pyrR1-pyrB loci. One was a prototroph with a deletion of both pyrR1 and the transcription attenuation site that resulted in large amounts of excreted pyrimidine nucleotides and increased intracellular UTP and CTP pools compared to wild-type levels. Low pyrimidine-independent expression of the pyr operon was obtained by antiterminator site-directed mutagenesis. The resulting AE1023 strain had reduced UTP and CTP pools and had the phenotype of a high-CO2-requiring auxotroph, since it was able to synthesize sufficient arginine and pyrimidines only in CO2-enriched air. Therefore, growth inhibition without CO2 enrichment may be due to low carbamoyl phosphate pools from lack of CPS activity.
Figures
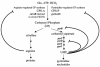

Similar articles
-
Expression of the pyr operon of Lactobacillus plantarum is regulated by inorganic carbon availability through a second regulator, PyrR2, homologous to the pyrimidine-dependent regulator PyrR1.J Bacteriol. 2006 Dec;188(24):8607-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00985-06. Epub 2006 Oct 13. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 17041052 Free PMC article.
-
Low carbamoyl phosphate pools may drive Lactobacillus plantarum CO2-dependent growth phenotype.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;14(1-3):22-30. doi: 10.1159/000107966. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 17957107 Review.
-
Uracil salvage pathway in Lactobacillus plantarum: Transcription and genetic studies.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jul;188(13):4777-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.00195-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16788187 Free PMC article.
-
In Lactobacillus plantarum, carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized by two carbamoyl-phosphate synthetases (CPS): carbon dioxide differentiates the arginine-repressed from the pyrimidine-regulated CPS.J Bacteriol. 2000 Jun;182(12):3416-22. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.12.3416-3422.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10852872 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pyrimidine biosynthetic gene expression in bacteria: repression without repressors.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008 Jun;72(2):266-300, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00001-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18535147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complete Reconstitution of the Vancomycin-Intermediate Staphylococcus aureus Phenotype of Strain Mu50 in Vancomycin-Susceptible S. aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 May 23;60(6):3730-42. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00420-16. Print 2016 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27067329 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pyr gene expression in Mycobacterium smegmatis by PyrR-dependent translational repression.J Bacteriol. 2007 Sep;189(17):6236-45. doi: 10.1128/JB.00803-07. Epub 2007 Jun 29. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17601781 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional response of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis DSM 20451T and its tcyB mutant lacking a functional cystine transporter to diamide stress.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Jul;80(14):4114-25. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00367-14. Epub 2014 May 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24795368 Free PMC article.
-
Interrelation between Tween and the membrane properties and high pressure tolerance of Lactobacillus plantarum.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Jul 13;18(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1203-y. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30001697 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of IR Biotyper for Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Typing and Its Application Potential in Probiotic Preliminary Screening.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 24;13:823120. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.823120. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35401469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouia, A., F. Bringel, L. Frey, A. Belarbi, A. Guyonvarch, B. Kammerer, and J. C. Hubert. 1990. Cloning and structure of the pyrE gene of Lactobacillus plantarum CCM 1904. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 57:233-238. - PubMed
-
- Bringel, F., and J. C. Hubert. 2003. Extent of genetic lesions of the arginine and pyrimidine biosynthetic pathways in Lactobacillus plantarum, L. paraplantarum, L. pentosus, and L. casei: prevalence of CO2 dependent auxotrophs and characterization of deficient arg genes in L. plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69:2674-2683. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

