Cyclooxygenase-2 and p53 expression as prognostic indicators in conventional renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 15744816
- PMCID: PMC2823039
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.1.133
Cyclooxygenase-2 and p53 expression as prognostic indicators in conventional renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
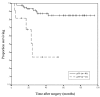
The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and p53 expression with prognosis in patients with conventional renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections of conventional RCC from 92 patients, who had undergone radical nephrectomy, were examined for COX-2 and p53 expression by immunohistochemistry and compared with clinicopathological variables. The COX-2 expression significantly correlated only with tumor size (p=0.049), whereas the p53 expression profoundly correlated with the TNM stage (p=0.024), M stage (p=0.001), and metastasis (synchronous or metachronous; p=0.004). The COX-2 overexpression did not significantly associate with p53 positivity (p=0.821). The survival rate of patients correlated with the p53 expression (p<0.0001) but not with the COX-2 expression (p=0.7506). Multivariate analyses indicated that tumor size, M stage, and p53 expression were independent prognostic factors for cancer-specific survival. The COX-2 expression was not an independent factor. These results show that the increased expression of p53 was associated with metastasis and a worse prognosis in conventional RCC, which suggests that p53 might have played an important role in the progression of conventional RCC. The increased expression of COX-2 was associated only with tumor size, but may not be an important prognostic factor in conventional RCC. No association was observed between COX-2 overexpression and p53 positivity in conventional RCC.
Figures



References
-
- Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL, Fraumeni JF., Jr Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA. 1999;281:1628–1631. - PubMed
-
- Delahunt B. Histopathologic prognostic indicators for renal cell carcinoma. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1998;15:68–76. - PubMed
-
- Yasunaga Y, Shin M, Miki T, Okuyama A, Aozasa K. Prognostic factors of renal cell carcinoma: a multivariate analysis. J Surg Oncol. 1998;68:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Vane JR, Bakhle YS, Botting RM. Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1998;38:97–120. - PubMed
-
- Herschman HR. Prostaglandin synthase 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1299:125–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

