Antioxidant effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in rats with advanced liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 15745444
- PMCID: PMC555751
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-5-7
Antioxidant effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in rats with advanced liver cirrhosis
Abstract
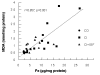
Background: The exogenous administration of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) induces hepatoprotective and antifibrogenic actions in experimental liver cirrhosis. To better understand the possible pathways behind the beneficial effect of IGF-I, the aim of this work was to investigate severe parameters involved in oxidative damage in hepatic tissue from cirrhotic animals treated with IGF-I (2 microg x 100 g(-1) x day(-1)). Iron and copper play an important role in oxidative mechanisms, producing the deleterious hydroxyl radical (*OH) that peroxides lipid membranes and damages DNA. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) and nitric oxide (NO) are known sources of free radicals and induce reduction of ferritin-Fe3+ into free Fe2+, contributing to oxidative damage.
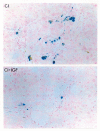
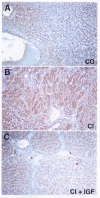
Methods: Liver cirrhosis was induced by CCl4 inhalation in Wistar male rats for 30 weeks. Healthy controls were studied in parallel (n = 10). Fe and Cu were assessed by atomic absoption spectrometry and iron content was also evaluated by Perls' staining. MPO was measured by ELISA and transferrin and ferritin by immunoturbidimetry. iNOS expression was studied by immuno-histochemistry.
Results: Liver cirrhosis was histologically proven and ascites was observed in all cirrhotic rats. Compared to controls untreated cirrhotic rats showed increased hepatic levels of iron, ferritin, transferrin (p < 0.01), copper, MPO and iNOS expression (p < 0.01). However, IGF-treatment induced a significant reduction of all these parameters (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: the hepatoprotective and antifibrogenic effects of IGF-I in cirrhosis are associated with a diminution of the hepatic contents of several factors all of them involved in oxidative damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antifibrogenic effect in vivo of low doses of insulin-like growth factor-I in cirrhotic rats.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 May 31;1536(2-3):185-95. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(01)00045-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11406353
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I restores the reduced somatostatinergic tone controlling growth hormone secretion in cirrhotic rats.Liver. 2001 Dec;21(6):405-9. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0676.2001.210607.x. Liver. 2001. PMID: 11903885
-
Liver transduction with a simian virus 40 vector encoding insulin-like growth factor I reduces hepatic damage and the development of liver cirrhosis.Gene Ther. 2007 Feb;14(3):203-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302858. Epub 2006 Oct 5. Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17024107
-
Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress.Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(10):1161-208. doi: 10.2174/0929867053764635. Curr Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 15892631 Review.
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Deficiency and Cirrhosis Establishment.J Clin Med Res. 2017 Apr;9(4):233-247. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2761w. Epub 2017 Feb 21. J Clin Med Res. 2017. PMID: 28270882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Regulation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jun 16;107(7):1812-1824. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac088. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35172328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotection and neuroprotection induced by low doses of IGF-II in aging rats.J Transl Med. 2011 Jul 6;9:103. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-103. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21733157 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin like growth factor-1 increases fatty liver preservation in IGL-1 solution.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Dec 7;16(45):5693-700. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5693. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21128318 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of IGF-I expression and anabolic signaling following ischemia/reperfusion in skeletal muscle of old mice.Exp Gerontol. 2011 Apr;46(4):265-72. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Exp Gerontol. 2011. PMID: 21094246 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial protection by low doses of insulin-like growth factor- I in experimental cirrhosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 May 7;14(17):2731-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2731. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18461658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sara VR, Hall K. Insulin-like growth factor-I and their binding proteins. Physiol Rew. 1990;70:591–613. - PubMed
-
- Caufriez A, Reding P, Urbain D, Goldstein J, Copinschi G. Insulin-like growth factor-I: a good indicator of functional hepatocelular capacity in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. J Endocrinol Invest. 1991;14:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Möller S, Becker U, Juul A, Skakkebæk NE, Christensen E, Group E. Prognostic Value of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I ans its Binding Proteins in patients with alcohol-induced Liver disease. Hepatology. 1996;23:1073–1078. - PubMed
-
- Schimpff RM, Lebrec D, Donadieu M. Somatomedin production in normal adults and cirrhotic patients. Acta Endocrinol. 1977;86:355–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

