The efficacy of playing a virtual reality game in modulating pain for children with acute burn injuries: a randomized controlled trial [ISRCTN87413556]
- PMID: 15745448
- PMCID: PMC554986
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-5-1
The efficacy of playing a virtual reality game in modulating pain for children with acute burn injuries: a randomized controlled trial [ISRCTN87413556]
Abstract
Background: The management of burn injuries is reported as painful, distressing and a cause of anxiety in children and their parents. Child's and parents' pain and anxiety, often contributes to extended time required for burns management procedures, in particular the process of changing dressings. The traditional method of pharmacologic analgesia is often insufficient to cover the burnt child's pain, and it can have deleterious side effects 12. Intervention with Virtual Reality (VR) games is based on distraction or interruption in the way current thoughts, including pain, are processed by the brain. Research on adults supports the hypothesis that virtual reality has a positive influence on burns pain modulation.
Methods: This study investigates whether playing a virtual reality game, decreases procedural pain in children aged 5-18 years with acute burn injuries. The paper reports on the findings of a pilot study, a randomised trial, in which seven children acted as their own controls though a series of 11 trials. Outcomes were pain measured using the self-report Faces Scale and findings of interviews with parent/carer and nurses.
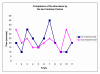
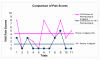
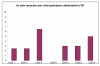
Results: The average pain scores (from the Faces Scale) for pharmacological analgesia only was, 4.1 (SD 2.9), while VR coupled with pharmacological analgesia, the average pain score was 1.3 (SD 1.8)
Conclusion: The study provides strong evidence supporting VR based games in providing analgesia with minimal side effects and little impact on the physical hospital environment, as well as its reusability and versatility, suggesting another option in the management of children's acute pain.
Figures

References
-
- Bonham A. Managing procedural pain in children with burns. Part 1: Assessment of pain in children. Int J Trauma Nurs. 1996;2:68–73. - PubMed
-
- McGrath PA, Gillispie J. Pain assessment in children and adolescents. Measurement of pain. In: Turk DC, Melzak R, editor. Handbook of pain assessment. 2. New York the Guilford Press; 2001. pp. 97–118.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

