Constitutional aneuploidy in the normal human brain
- PMID: 15745943
- PMCID: PMC6726097
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4560-04.2005
Constitutional aneuploidy in the normal human brain
Abstract
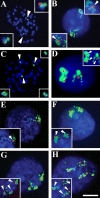
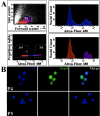
The mouse brain contains genetically distinct cells that differ with respect to chromosome number manifested as aneuploidy (Rehen et al., 2001); however, the relevance to humans is not known. Here, using double-label fluorescence in situ hybridization for the autosome chromosome 21 (chromosome 21 point probes combined with chromosome 21 "paint" probes), along with immunocytochemistry and cell sorting, we present evidence for chromosome gain and loss in the human brain. Chromosome 21 aneuploid cells constitute approximately 4% of the estimated one trillion cells in the human brain and include non-neuronal cells and postmitotic neurons identified by the neuronspecific nuclear protein marker. In comparison, human interphase lymphocytes present chromosome 21 aneuploidy rates of 0.6%. Together, these data demonstrate that human brain cells (both neurons and non-neuronal cells) can be aneuploid and that the resulting genetic mosaicism is a normal feature of the human CNS.
Figures
References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1994) Current protocols in molecular biology. New York: Wiley.
-
- Barch MJ, Knutsen T, Spurbeck JL (1997) The AGT cytogenetics laboratory manual. Philadelphia: Lippincott.
-
- Bhattacharyya A, Svendsen CN (2003) Human neural stem cells: a new tool for studying cortical development in Down's syndrome. Genes Brain Behav 2: 179186. - PubMed
-
- Bitoun P, Martin-Pont B, Tamboise E, Gaudelus J (1994) Optic atrophy, microcephaly, mental retardation and mosaic variegated aneuploidy: a human mitotic mutation. Ann Genet 37: 75-77. - PubMed
-
- Geller LN, Potter H (1999) Chromosome missegregation and trisomy 21 mosaicism in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 6: 167-179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
