Neurosteroid-induced plasticity of immature synapses via retrograde modulation of presynaptic NMDA receptors
- PMID: 15745954
- PMCID: PMC6726098
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3877-04.2005
Neurosteroid-induced plasticity of immature synapses via retrograde modulation of presynaptic NMDA receptors
Abstract
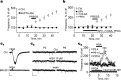
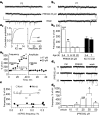
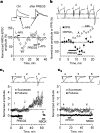
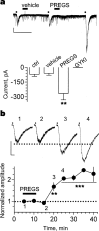
Neurosteroids are produced de novo in neuronal and glial cells, which begin to express steroidogenic enzymes early in development. Studies suggest that neurosteroids may play important roles in neuronal circuit maturation via autocrine and/or paracrine actions. However, the mechanism of action of these agents is not fully understood. We report here that the excitatory neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate induces a long-lasting strengthening of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal neurons during a restricted developmental period. Using the acute hippocampal slice preparation and patch-clamp electrophysiological techniques, we found that pregnenolone sulfate increases the frequency of AMPA-mediated miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons. This effect could not be observed in slices from rats older than postnatal day 5. The mechanism of action of pregnenolone sulfate involved a short-term increase in the probability of glutamate release, and this effect is likely mediated by presynaptic NMDA receptors containing the NR2D subunit, which is transiently expressed in the hippocampus. The increase in glutamate release triggered a long-term enhancement of AMPA receptor function that requires activation of postsynaptic NMDA receptors containing NR2B subunits. Importantly, synaptic strengthening could also be triggered by postsynaptic neuron depolarization, and an anti-pregnenolone sulfate antibody scavenger blocked this effect. This finding indicates that a pregnenolone sulfate-like neurosteroid is a previously unrecognized retrograde messenger that is released in an activity-dependent manner during development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pregnenolone sulfate enhances spontaneous glutamate release by inducing presynaptic Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release.Neuroscience. 2010 Nov 24;171(1):106-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.07.057. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20816925
-
Diminished neuronal activity increases neuron-neuron connectivity underlying silent synapse formation and the rapid conversion of silent to functional synapses.J Neurosci. 2005 Apr 20;25(16):4040-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4115-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15843606 Free PMC article.
-
Retrograde activation of presynaptic NMDA receptors enhances GABA release at cerebellar interneuron-Purkinje cell synapses.Nat Neurosci. 2004 May;7(5):525-33. doi: 10.1038/nn1227. Epub 2004 Apr 18. Nat Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15097992
-
Modulation of glutamatergic transmission by sulfated steroids: role in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder.Brain Res Rev. 2008 Mar;57(2):506-19. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.04.009. Epub 2007 May 3. Brain Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 17597219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscarinic Receptors, from Synaptic Plasticity to its Role in Network Activity.Neuroscience. 2021 Feb 21;456:60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 32278062 Review.
Cited by
-
Preferential Inhibition of Tonically over Phasically Activated NMDA Receptors by Pregnane Derivatives.J Neurosci. 2016 Feb 17;36(7):2161-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3181-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26888927 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Oct;73(4):298-487. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000131. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34753794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic NMDA receptors - dynamics and distribution in developing axons in vitro and in vivo.J Cell Sci. 2015 Feb 15;128(4):768-80. doi: 10.1242/jcs.162362. Epub 2014 Dec 19. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 25526735 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental switch in the contribution of presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDA receptors to long-term depression.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 12;27(37):9835-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5494-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17855598 Free PMC article.
-
Developmentally regulated actions of alcohol on hippocampal glutamatergic transmission.J Neurosci. 2005 Aug 31;25(35):8027-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2434-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16135760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baulieu EE, Robel P, Schumacher M (2001) Neurosteroids: beginning of the story. Int Rev Neurobiol 46: 1-32. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y (2002) Excitatory actions of GABA during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 728-739. - PubMed
-
- Berretta N, Jones RS (1996) Tonic facilitation of glutamate release by presynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate autoreceptors in the entorhinal cortex. Neuroscience 75: 339-344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
