Reduced nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in kinin B1 receptor knock-out mice
- PMID: 15745967
- PMCID: PMC6726078
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2466-04.2005
Reduced nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in kinin B1 receptor knock-out mice
Abstract
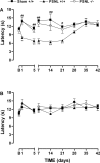
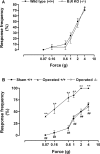
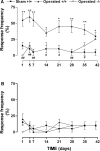
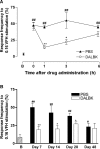
Injury to peripheral nerves often results in a persistent neuropathic pain condition that is characterized by spontaneous pain, allodynia, and hyperalgesia. Nerve injury is accompanied by a local inflammatory reaction in which nerve-associated and immune cells release several pronociceptive mediators. Kinin B1 receptors are rarely expressed in nontraumatized tissues, but they can be expressed after tissue injury. Because B1 receptors mediate chronic inflammatory painful processes, we studied their participation in neuropathic pain using receptor gene-deleted mice. In the absence of neuropathy, we found no difference in the paw-withdrawal responses to thermal or mechanical stimulation between B1 receptor knock-out mice and 129/J wild-type mice. Partial ligation of the sciatic nerve in the wild-type mouse produced a profound and long-lasting decrease in thermal and mechanical thresholds in the paw ipsilateral to nerve lesion. Threshold changed neither in the sham-operated animals nor in the paw contralateral to lesion. Ablation of the gene for the B1 receptor resulted in a significant reduction in early stages of mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Furthermore, systemic treatment with the B1 selective receptor antagonist des-Arg9-[Leu8]-bradykinin reduced the established mechanical allodynia observed 7-28 d after nerve lesion in wild-type mice. Partial sciatic nerve ligation induced an upregulation in B1 receptor mRNA in ipsilateral paw, sciatic nerve, and spinal cord of wild-type mice. Together, kinin B1 receptor activation seems to be essential to neuropathic pain development, suggesting that an oral-selective B1 receptor antagonist might have therapeutic potential in the management of chronic pain.
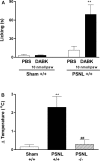
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peripheral kinin B(1) and B(2) receptor-operated mechanisms are implicated in neuropathic nociception induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Jul;53(1):48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.04.013. Epub 2007 May 3. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17555775
-
Amelioration of hyperalgesia by kinin receptor antagonists or kininogen deficiency in chronic constriction nerve injury in rats.Inflamm Res. 2003 Apr;52(4):164-9. doi: 10.1007/s000110300067. Inflamm Res. 2003. PMID: 12755382
-
The role of kinin B1 receptors in the nociception produced by peripheral protein kinase C activation in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Mar;54(3):597-604. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.11.008. Epub 2007 Nov 22. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18164734
-
Kinin B1 receptors: key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Dec;143(7):803-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706012. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15520046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of Flavonoids on Peripheral Neuropathic Pain.Molecules. 2020 Mar 5;25(5):1171. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051171. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32150953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Food-Derived Natural Compounds for Pain Relief in Neuropathic Pain.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7917528. doi: 10.1155/2016/7917528. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27891521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-nociceptive effect of stigmasterol in mouse models of acute and chronic pain.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;390(11):1163-1172. doi: 10.1007/s00210-017-1416-x. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28821921
-
A phenotypic screening platform for chronic pain therapeutics using all-optical electrophysiology.Pain. 2024 Apr 1;165(4):922-940. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003090. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Pain. 2024. PMID: 37963235 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of Paclitaxel-Induced Pain Syndrome in Mice by Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Involvement of Kinins.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Dec;54(10):7824-7837. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0275-7. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27844290
-
Bradykinin receptor expression and bradykinin-mediated sensitization of human sensory neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 1:2023.03.31.534820. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.31.534820. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Pain. 2024 Jan 1;165(1):202-215. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003013. PMID: 37034782 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Argañaraz GA, Silva Jr JA, Perosa SR, Pessoa LG, Carvalho FF, Bascands JL, Bader M, Trindade ES, Amado D, Cavalheiro EA, Pesquero JB, Naffah-Mazzacoratti MG (2004) The synthesis and distribution of the kinin B1 and B2 receptors are modified in the hippocampus of rats submitted to pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Brain Res 1006: 114-125. - PubMed
-
- Besson JM (1999) The neurobiology of pain. Lancet 353: 1610-1615. - PubMed
-
- Blair SJ, Chinthagada M, Hoppenstehdt D, Kijowski R, Fareed J (1998) Role of neuropeptides in pathogenesis of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Acta Orthop Bel 64: 448-451. - PubMed
-
- Borkowski JA, Ranson RW, Seabrook GR, Trumbauer M, Chen H, Hill RG, Strader CD, Hess JF (1995) Targeted disruption of a B2 bradykinin receptor in mice eliminates bradykinin action in smooth muscle and neurons. J Biol Chem 270: 13706-13710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
