Emergent autoimmunity in graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 15746077
- PMCID: PMC1894995
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4980
Emergent autoimmunity in graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
Donor T-cell recognition of host alloantigens presented by host antigen-presenting cells (APCs) is necessary for the induction of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), but whether direct alloreactivity is sufficient for the propagation of GVHD is unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that GVHD cannot be effectively propagated through the direct pathway of allorecognition. Rather, donor T-cell recognition of antigens through the indirect pathway is necessary for the perpetuation of GVHD. Furthermore, GVHD results in the breaking of self tolerance, resulting in the emergence of donor T cells that can cause autoimmune disease in syngeneic recipients. Notably, GVHD-induced autoreactivity is donor APC dependent, transferable into secondary hosts, and involves cells of the innate immune system. These results indicate that donor T-cell--mediated pathologic damage during GVHD becomes donor APC dependent and provide a mechanistic explanation for the long-standing observation that GVHD is associated with autoimmune clinical manifestations.
Figures
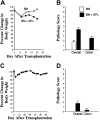
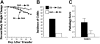
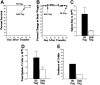
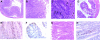
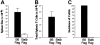
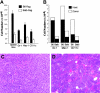
References
-
- Ferrara JLM, Deeg HJ, Burakoff S. Graft versus host disease. New York: Marcell Dekker, 1997.
-
- Reddy P. Pathophysiology of acute graft-versus-host disease. Hematol Oncol. 2003;21: 149-161. - PubMed
-
- Higman MA, Vogelsang GB. Chronic graft versus host disease. Br J Haematol. 2004;125: 435-454. - PubMed
-
- Rouquette-Gally AM, Boyeldieu D, Prost AC, Gluckman E. Autoimmunity after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. A study of 53 long-term-surviving patients. Transplantation. 1988;46: 238-240. - PubMed
-
- Rouquette-Gally AM, Boyeldieu D, Gluckman E, Abuaf N, Combrisson A. Autoimmunity in 28 patients after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: comparison with Sjogren syndrome and scleroderma. Br J Haematol. 1987;66: 45-47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

