Prolactin and estrogen enhance the activity of activating protein 1 in breast cancer cells: role of extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2-mediated signals to c-fos
- PMID: 15746191
- PMCID: PMC1630766
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2004-0339
Prolactin and estrogen enhance the activity of activating protein 1 in breast cancer cells: role of extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2-mediated signals to c-fos
Abstract
Despite the important roles of both prolactin (PRL) and 17beta-estradiol (E2) in normal mammary development as well as in breast cancer, and coexpression of the estrogen receptor (ER) and PRL receptor in many mammary tumors, the interactions between PRL and E2 in breast cancer have not been well studied. The activating protein 1 (AP-1) transcription factor, a known regulator of processes essential for normal growth and development as well as carcinogenesis, is a potential site for cross-talk between these hormones in breast cancer cells. Here we demonstrate that PRL and E2 cooperatively enhance the activity of AP-1 in MCF-7-derived cells. In addition to the acute PRL-induced ERK1/2 activation, PRL and E2 also individually elicited delayed, sustained rises in levels of phosphorylated p38 and especially ERK1/2. Together, these hormones increased the dynamic phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and c-Fos, and induced c-fos promoter activity. Synergistic activation of the transcription factor, Elk-1, reflected the PRL-E2 interaction at ERK1/2 and is a likely mechanism for activation of the c-fos promoter via the serum response element. The enhanced AP-1 activity resulting from the interaction of these hormones may increase expression of many target genes that are critical for oncogenesis and may contribute to neoplastic progression.
Figures



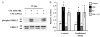
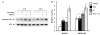


Similar articles
-
Multiple kinase cascades mediate prolactin signals to activating protein-1 in breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Dec;18(12):3064-75. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0187. Epub 2004 Aug 19. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15319452 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin modulates phosphorylation, signaling and trafficking of epidermal growth factor receptor in human T47D breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2006 Dec 7;25(58):7565-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209740. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16785991
-
SIRT1 is involved in oncogenic signaling mediated by GPER in breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jul 30;6(7):e1834. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.201. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26225773 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosyl phosphorylated serine-threonine kinase PAK1 is a novel regulator of prolactin-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;846:97-137. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25472536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in experimental models of breast cancer progression and in mammary gland development.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):209. doi: 10.1186/bcr2361. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19818165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global profiling of prolactin-modulated transcripts in breast cancer in vivo.Mol Cancer. 2013 Jun 12;12:59. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-59. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23758962 Free PMC article.
-
17β-estradiol up-regulates miR-155 expression and reduces TP53INP1 expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Jul;379(1-2):201-11. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1642-6. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23568502
-
Breast Cancer and Prolactin - New Mechanisms and Models.Endocrinology. 2022 Oct 1;163(10):bqac122. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqac122. Endocrinology. 2022. PMID: 35922139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling prolactin actions in breast cancer in vivo: insights from the NRL-PRL mouse.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;846:201-20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25472540 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of miR-106b in tumorigenic actions of both prolactin and estradiol.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(22):36368-36382. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16755. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horseman ND. Prolactin and mammary gland development. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1999;4:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Grimm SL, Seagroves TN, Kabotyanski EB, Hovey RC, Vonderhaar BK, Lydon JP, Miyoshi K, Hennighausen L, Ormandy CJ, Lee AV, Stull MA, Wood TL, Rosen JM. Disruption of steroid and prolactin receptor patterning in the mammary gland correlates with a block in lobuloalveolar development. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:2675–2691. - PubMed
-
- Shyamala G, Chou YC, Louie SG, Guzman RC, Smith GH, Nandi S. Cellular expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors in mammary glands: regulation by hormones, development and aging. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;80:137–148. - PubMed
-
- Hovey RC, Trott JF, Ginsburg E, Goldhar A, Sasaki MM, Fountain SJ, Sundararajan K, Vonderhaar BK. Transcriptional and spatiotemporal regulation of prolactin receptor mRNA and cooperativity with progesterone receptor function during ductal branch growth in the mammary gland. Dev Dyn. 2001;222:192–205. - PubMed
-
- Couse JF, Korach KS. Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev. 1999;20:358–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

