C/EBPalpha activates the transcription of triacylglycerol hydrolase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 15752068
- PMCID: PMC1183477
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041442
C/EBPalpha activates the transcription of triacylglycerol hydrolase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
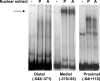
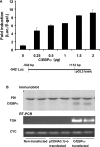
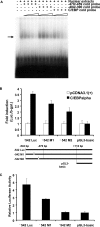
TGH (triacylglycerol hydrolase) catalyses the lipolysis of intracellular stored triacylglycerol. To explore the mechanisms that regulate TGH expression in adipose tissue, we studied the expression of TGH during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. TGH mRNA and protein levels increased dramatically in 3T3-L1 adipocytes compared with pre-adipocytes. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated enhanced binding of nuclear proteins of adipocytes to the distal murine TGH promoter region (-542/-371 bp), yielding one adipocyte-specific migrating complex. Competitive and supershift assays demonstrated that the distal TGH promoter fragment bound C/EBPalpha (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha). Transient transfections of different mutant TGH promoter-luciferase constructs into 3T3-L1 adipocytes and competitive electromobility shift assays showed that the C/EBP-binding elements at positions -470/-459 bp and -404/-390 bp are important for transcriptional activation. Co-transfection with C/EBPalpha cDNA and TGH promoter constructs in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes demonstrated that C/EBPalpha increased TGH promoter activity. Ectopic expression of C/EBPalpha in NIH 3T3 cells activated TGH mRNA expression without causing differentiation into adipocytes. These experiments directly link increased TGH expression in adipocytes to transcriptional regulation by C/EBPalpha. This is the first evidence that C/EBPalpha participates directly in the regulation of an enzyme associated with lipolysis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sequential gene promoter interactions by C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha, and PPARgamma during adipogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 May 21;318(1):213-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.017. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15110775
-
Upstream stimulatory factors regulate the C/EBP alpha gene during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Mar 9;354(2):517-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.008. Epub 2007 Jan 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17239350
-
Ectopic expression of Neuronatin potentiates adipogenesis through enhanced phosphorylation of cAMP-response element-binding protein in 3T3-L1 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Nov 18;337(2):481-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.09.078. Epub 2005 Sep 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16223607
-
Role of the CCAAT enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs) in adipocyte differentiation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Dec 29;266(3):677-83. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1885. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10603305 Review.
-
Triacylglycerol hydrolase: role in intracellular lipid metabolism.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Jul;61(13):1633-51. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-3426-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15224187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of RIFL, a novel adipocyte-enriched insulin target gene with a role in lipid metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Aug 1;303(3):E334-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00084.2012. Epub 2012 May 8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22569073 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxylesterases in lipid metabolism: from mouse to human.Protein Cell. 2018 Feb;9(2):178-195. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0437-z. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Protein Cell. 2018. PMID: 28677105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes.Annu Rev Nutr. 2007;27:79-101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.27.061406.093734. Annu Rev Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17313320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bisphenol A-mediated suppression of LPL gene expression inhibits triglyceride accumulation during adipogenic differentiation of human adult stem cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036109. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662114 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of adipocyte differentiation and lipid metabolism by novel synthetic chromenes exploring anti-obesity and broader therapeutic potential.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 3;15(1):4051. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87945-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39900791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Londos C., Brasaemle D. L., Schultz C. J., Adler-Wailes D. C., Levin D. M., Kimmel A. R., Rondinone C. M. On the control of lipolysis in adipocytes. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1999;892:155–168. - PubMed
-
- Krey G., Braissant O., L'Horset F., Kalkhoven E., Perroud M., Parker M. G., Wahli W. Fatty acids, eicosanoids, and hypolipidemic agents identified as ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors by coactivator-dependent receptor ligand assay. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997;11:779–791. - PubMed
-
- Holm C., Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Fredrikson G., Nilsson S., Miller C. G., Shively J. E., Heinzmann C., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., et al. Hormone-sensitive lipase: sequence, expression, and chromosomal localization to 19 cent-q13.3. Science. 1988;241:1503–1506. - PubMed
-
- Carey G. B. Mechanisms regulating adipocyte lipolysis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998;441:157–170. - PubMed
-
- Okazaki H., Osuga J., Tamura Y., Yahagi N., Tomita S., Shionoiri F., Iizuka Y., Ohashi K., Harada K., Kimura S., et al. Lipolysis in the absence of hormone-sensitive lipase: evidence for a common mechanism regulating distinct lipases. Diabetes. 2002;51:3368–3375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

