A HEV-restricted sulfotransferase is expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovium and is induced by lymphotoxin-alpha/beta and TNF-alpha in cultured endothelial cells
- PMID: 15752429
- PMCID: PMC1079838
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-6-6
A HEV-restricted sulfotransferase is expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovium and is induced by lymphotoxin-alpha/beta and TNF-alpha in cultured endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: The recruitment of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs relies on interactions of circulating cells with high endothelial venules (HEV). HEV are exclusive to these organs under physiological conditions, but they can develop in chronically-inflamed tissues. The interaction of L-selectin on lymphocytes with sulfated glycoprotein ligands on HEV results in lymphocyte rolling, which represents the initial step in lymphocyte homing. HEV expression of GlcNAc6ST-2 (also known as HEC-GlcNAc6ST, GST-3, LSST or CHST4), an HEV-restricted sulfotransferase, is essential for the elaboration of L-selectin functional ligands as well as a critical epitope recognized by MECA-79 mAb.
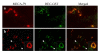
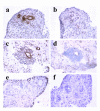
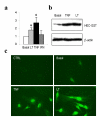
Results: We examined the expression of GlcNAc6ST-2 in relationship to the MECA-79 epitope in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial vessels. Expression of GlcNAc6ST-2 was specific to RA synovial tissues as compared to osteoarthritis synovial tissues and localized to endothelial cells of HEV-like vessels and small flat-walled vessels. Double MECA-79 and GlcNAc6ST-2 staining showed colocalization of the MECA-79 epitope and GlcNAc6ST-2. We further found that both TNF-alpha and lymphotoxin-alphabeta induced GlcNAc6ST-2 mRNA and protein in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Conclusion: These observations demonstrate that GlcNAc6ST-2 is induced in RA vessels and provide potential cytokine pathways for its induction. GlcNAc6ST-2 is a novel marker of activated vessels within RA ectopic lymphoid aggregates. This enzyme represents a potential therapeutic target for RA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of a sulfotransferase (HEC-GlcNAc6ST) in high endothelial venules of lymph nodes and in high endothelial venule-like vessels within ectopic lymphoid aggregates: relationship to the MECA-79 epitope.Am J Pathol. 2004 May;164(5):1635-44. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63722-4. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15111310 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of PNAd and N-acetylglucosamine 6-O-sulfotransferases 1 and 2 in mouse collagen-induced arthritis.BMC Immunol. 2006 Jun 13;7:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-7-12. BMC Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16772045 Free PMC article.
-
Preferential induction of peripheral lymph node addressin on high endothelial venule-like vessels in the active phase of ulcerative colitis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jul;102(7):1499-509. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01189.x. Epub 2007 Apr 24. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17459027
-
Role of sulfated O-glycans expressed by high endothelial venule-like vessels in pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 May;32(5):774-9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.774. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19420741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfated L-selectin ligands as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation.Trends Immunol. 2006 Dec;27(12):559-65. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.10.007. Epub 2006 Oct 17. Trends Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17049924 Review.
Cited by
-
Human synovial lubricin expresses sialyl Lewis x determinant and has L-selectin ligand activity.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):35922-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.363119. Epub 2012 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22930755 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Two distinct lymphocyte homing systems involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases.Semin Immunopathol. 2012 May;34(3):401-13. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0302-3. Epub 2012 May 10. Semin Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 22572886 Review.
-
The LINC00452/miR-204/CHST4 Axis Regulating Thymic Tregs Might Be Involved in the Progression of Thymoma-Associated Myasthenia Gravis.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 30;13:828970. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.828970. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35432149 Free PMC article.
-
High endothelial venules (HEVs) in immunity, inflammation and cancer.Angiogenesis. 2021 Nov;24(4):719-753. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09792-8. Epub 2021 May 6. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33956259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Cell Infiltration and Tertiary Lymphoid Structures as Determinants of Antitumor Immunity.J Immunol. 2018 Jan 15;200(2):432-442. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701269. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29311385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takemura S, Braun A, Crowson C, Kurtin PJ, Cofield RH, O'Fallon WM, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Lymphoid neogenesis in rheumatoid synovitis. J Immunol. 2001;167:1072–1080. - PubMed
-
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Ectopic germinal center formation in rheumatoid synovitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;987:140–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

