Ethylene signal transduction
- PMID: 15753119
- PMCID: PMC4246747
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mci100
Ethylene signal transduction
Abstract
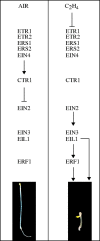
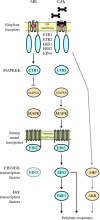
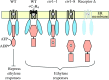
Background: The phytohormone ethylene is a key regulator of plant growth and development. Components of the pathway for ethylene signal transduction were identified by genetic approaches in Arabidopsis and have now been shown to function in agronomically important plants as well.
Scope: This review focuses on recent advances in our knowledge on ethylene signal transduction, in particular on recently proposed components of the pathway, on the interaction between the pathway components and on the roles of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation in ethylene signalling.
Conclusions: Data indicate that the site of ethylene perception is at the endoplasmic reticulum and point to the importance of protein complexes in mediating the initial steps in ethylene signal transduction. The expression level of pathway components is regulated by both transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms, degradation of the transcription factor EIN3 being a primary means by which the sensitivity of plants to ethylene is regulated. EIN3 also represents a control point for cross-talk with other signalling pathways, as exemplified by the effects of glucose upon its expression level. Amplification of the initial ethylene signal is likely to play a significant role in signal transduction and several mechanisms exist by which this may occur based on properties of known pathway components. Signal output from the pathway is mediated in part by carefully orchestrated changes in gene expression, the breadth of these changes now becoming clear through expression analysis using microarrays.
Figures
References
-
- Abeles FB, Morgan PW, Saltveit Jr ME. 1992.Ethylene in plant biology, 2nd edn. San Diego: Academic Press.
-
- Adams-Phillips L, Barry C, Giovannoni J. 2004. Signal transduction systems regulating fruit ripening. Trends in Plant Science 9: 331–338. - PubMed
-
- Adams-Phillips L, Barry C, Kannan P, Leclercq J, Bouzayen M, Giovannoni J. 2004. Evidence that CTR1-mediated ethylene signal transduction in tomato is encoded by a multigene family whose members display distinct regulatory features. Plant Molecular Biology 54: 387–404. - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Ecker JR. 2001. The ethylene pathway: a paradigm for plant hormone signalling and interaction. Science STKE 2001: RE1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

