Essential role for interleukin-2 for CD4(+)CD25(+) T regulatory cell development during the neonatal period
- PMID: 15753210
- PMCID: PMC2212835
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041179
Essential role for interleukin-2 for CD4(+)CD25(+) T regulatory cell development during the neonatal period
Abstract
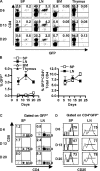
Although many aspects of CD4(+)CD25(+) T regulatory (T(reg)) cell development remain largely unknown, signaling through the IL-2R represents one feature for the production of T(reg) cells. Therefore, the present study was undertaken to further define early developmental steps in the production of T(reg) cells, including a more precise view on the role of interleukin (IL)-2 in this process. After adoptive transfer of wild-type T(reg) cells into neonatal IL-2Rbeta(-/-) mice, only a small fraction of donor T(reg) cells selectively seeded the lymph node (LN). These donor T(reg) cells underwent rapid and extensive IL-2-dependent proliferation, followed by subsequent trafficking to the spleen. Thus, IL-2 is essential for T(reg) cell proliferation in neonatal LN. The number and distribution of T(reg) cells in the periphery of normal neonatal mice closely paralleled that seen for IL-2Rbeta(-/-) mice that received T(reg) cells. However, for normal neonates, blockade of IL-2 decreased T(reg) cells in both the thymus and LN. Therefore, two steps of T(reg) cell development depend upon IL-2 in neonatal mice, thymus production, and subsequent expansion in the LN.
Figures


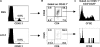

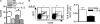
Similar articles
-
CD4 regulatory T cells prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2Rbeta-deficient mice. Implications for the nonredundant function of IL-2.Immunity. 2002 Aug;17(2):167-78. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00367-9. Immunity. 2002. PMID: 12196288
-
Function of the IL-2R for thymic and peripheral CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ T regulatory cells.J Immunol. 2007 Apr 1;178(7):4062-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4062. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17371960
-
CD40/CD40L interaction regulates CD4+CD25+ T reg homeostasis through dendritic cell-produced IL-2.Eur J Immunol. 2005 Feb;35(2):557-67. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425810. Eur J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15682445
-
T cells that cannot respond to TGF-beta escape control by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells.J Exp Med. 2005 Mar 7;201(5):737-46. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040685. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 15753207 Free PMC article.
-
Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.Semin Immunol. 2004 Apr;16(2):89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2003.12.005. Semin Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15036232 Review.
Cited by
-
Dendritic cells in the periphery control antigen-specific natural and induced regulatory T cells.Front Immunol. 2013 Jun 21;4:151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00151. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23801989 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis of CD4+ CD25(high) T cells in type 1 diabetes may be partially mediated by IL-2 deprivation.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 5;4(8):e6527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006527. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19654878 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IL-2: an unexpected effect in treating immunological diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018 Jan 19;3:2. doi: 10.1038/s41392-017-0002-5. eCollection 2018. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018. PMID: 29527328 Free PMC article.
-
The Lower Limit of Regulatory CD4+ Foxp3+ TCRβ Repertoire Diversity Required To Control Autoimmunity.J Immunol. 2017 Apr 15;198(8):3127-3135. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601966. Epub 2017 Mar 6. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28264971 Free PMC article.
-
Development of regulatory T cells requires IL-7Ralpha stimulation by IL-7 or TSLP.Blood. 2008 Oct 15;112(8):3283-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-137414. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18664628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shevach, E.M. 2000. Regulatory T cells in autoimmmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:423–449. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi, S. 2000. Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 101:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Jordan, M.S., A. Boesteanu, A.J. Reed, A.L. Petrone, A.E. Holenbeck, M.A. Lerman, A. Naji, and A.J. Caton. 2001. Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat. Immunol. 2:301–306. - PubMed
-
- Apostolou, I., A. Sarukhan, L. Klein, and H. von Boehmer. 2002. Origin of regulatory T cells with known specificity for antigen. Nat. Immunol. 3:756–763. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot, J.D., M.A. Gavin, and A.Y. Rudensky. 2003. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 4:330–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

