Application of monoclonal antibodies in functional and comparative investigations of heavy-chain immunoglobulins in new world camelids
- PMID: 15753251
- PMCID: PMC1065209
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.12.3.380-386.2005
Application of monoclonal antibodies in functional and comparative investigations of heavy-chain immunoglobulins in new world camelids
Abstract
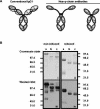
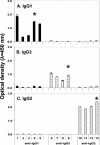
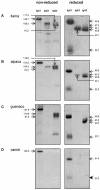
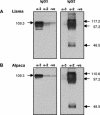
Of the three immunoglobulin G (IgG) isotypes described to occur in camelids, IgG2 and IgG3 are distinct in that they do not incorporate light chains. These heavy-chain antibodies (HCAbs) constitute approximately 50% of the IgG in llama serum and as much as 75% of the IgG in camel serum. We have produced isotype-specific mouse monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in order to investigate the roles of HCAbs in camelid immunity. Seventeen stable hybridomas were cloned, and three MAbs that were specific for epitopes on the gamma chains of llama IgG1, IgG2, or IgG3 were characterized in detail. Affinity chromatography revealed that each MAb bound its isotype in solution in llama serum. The antibodies bound to the corresponding alpaca IgGs, to guanaco IgG1 and IgG2, and to camel IgG1. Interestingly, anti-IgG2 MAbs bound three heavy-chain species in llama serum, confirming the presence of three IgG2 subisotypes. Two IgG2 subisotypes were detected in alpaca and guanaco sera. The MAbs detected llama serum IgGs when they were bound to antigen in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and were used to discern among isotypes induced during infection with a parasitic nematode. Diseased animals, infected with Parelaphostrongylus tenuis, did not produce antigen-specific HCAbs; rather, they produced the conventional isotype, IgG1, exclusively. Our data document the utility of these MAbs in functional and physiologic investigations of the immune systems of New World camelids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TNT detection using llama antibodies and a two-step competitive fluid array immunoassay.J Immunol Methods. 2008 Nov 30;339(1):47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Aug 26. J Immunol Methods. 2008. PMID: 18755196
-
Immunobiological role of llama heavy-chain antibodies against a bacterial beta-lactamase.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2007 Jun 15;117(3-4):173-82. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2007.03.003. Epub 2007 Mar 18. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2007. PMID: 17448545
-
Contributions of conventional and heavy-chain IgG to immunity in fetal, neonatal, and adult alpacas.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010 Dec;17(12):2007-15. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00287-10. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20926693 Free PMC article.
-
[Heavy-chain antibodies of the Camelidae and their possible applications].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2005 May 16;59:193-202. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2005. PMID: 15928603 Review. Polish.
-
Camelid immunoglobulins and their importance for the new-born--a review.J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2001 Oct;48(8):561-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0450.2001.00478.x. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2001. PMID: 11708675 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of heavy-chain antibody responses and resistance to Parelaphostrongylus tenuis in experimentally infected alpacas.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Jul;19(7):1019-26. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00178-12. Epub 2012 May 16. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22593238 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of rabbit polyclonal antibody against camel recombinant nanobodies.Open Life Sci. 2022 Jun 15;17(1):659-675. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0065. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35800073 Free PMC article.
-
Alpaca (Lama pacos) as a convenient source of recombinant camelid heavy chain antibodies (VHHs).J Immunol Methods. 2007 Jul 31;324(1-2):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2007.04.008. Epub 2007 May 15. J Immunol Methods. 2007. PMID: 17568607 Free PMC article.
-
Llama peripheral B-cell populations producing conventional and heavy chain-only IgG subtypes are phenotypically indistinguishable but immunogenetically distinct.Immunogenetics. 2019 Apr;71(4):307-320. doi: 10.1007/s00251-018-01102-9. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Immunogenetics. 2019. PMID: 30656359
-
Camelid Single-Domain Antibodies: Promises and Challenges as Lifesaving Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 30;23(9):5009. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095009. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azwai, S. M., S. D. Carter, and Z. Woldehiwet. 1995. Monoclonal antibodies against camel (Camelus dromedarius) IgG, IgM and light chains. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 45:175-184. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, J. K., and L. G. Rickard. 1987. Fecal survey of llamas (Lama glama) in Oregon: incidental recovery of Nematodirus battus. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 191:1579-1581. - PubMed
-
- Conrath, K. E., U. Wernery, S. Muyldermans, and V. K. Nguyen. 2003. Emergence and evolution of functional heavy-chain antibodies in Camelidae. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 27:87-103. - PubMed
-
- Cortez-Retamozo, V., M. Lauwereys, G. G. Hassanzadeh, M. Gobert, K. Conrath, S. Muyldermans, P. De Baetselier, and H. Revets. 2002. Efficient tumor targeting by single-domain antibody fragments of camels. Int. J. Cancer 98:456-462. - PubMed
-
- Desmyter, A., K. Decanniere, S. Muyldermans, and L. Wyns. 2001. Antigen specificity and high affinity binding provided by one single loop of a camel single-domain antibody. J. Biol. Chem. 276:26285-26290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

