Enhanced cocaine responsiveness and impaired motor coordination in metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2 knockout mice
- PMID: 15753323
- PMCID: PMC554835
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0500914102
Enhanced cocaine responsiveness and impaired motor coordination in metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2 knockout mice
Abstract
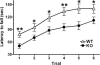
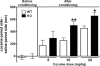
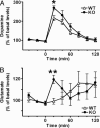
Extensive pharmacological studies have recently emerged indicating that group 2 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) comprising mGluR2 and mGluR3 subtypes are associated with several neurological and psychiatric disorders. mGluR2 is widely distributed both presynaptically and postsynaptically in a variety of neuronal cells, but the physiological role of mGluR2 in brain function is poorly understood. This investigation involves a comprehensive behavioral analysis of mGluR2-/- knockout (KO) mice to explore the physiological role of mGluR2 in brain function. Although, under general observation, mGluR2-/- KO mice appeared to have no behavioral abnormalities, they exhibited several lines of behavioral alterations in the enforcing and defined behavioral tests. They showed a significant increase in locomotor sensitization and conditioned place preference in association with repeated cocaine administration, indicating that mGluR2 contributes to behavioral responses implicated in reinforcement and addiction of cocaine. Upon in vivo microdialysis analysis after cocaine administration, not only did extracellular levels of dopamine increase but also the response pattern of glutamate release markedly changed in the nucleus accumbens of mGluR2-/- KO mice. The mGluR2-/- KO mice also showed significant impairment in motor coordination in the accelerating rota-rod test and exhibited hyperlocomotion in novel environmental and stressful conditions, when assessed by the open-field and forced-swim tests. These results indicate that the inhibitory mGluR2 plays a pivotal role in synaptic regulation of glutamatergic transmission in the neural network.
Figures

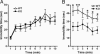

Similar articles
-
Altered sensitivities to morphine and cocaine in scaffold protein tamalin knockout mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 11;104(37):14789-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706945104. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17766434 Free PMC article.
-
Use of MGLUR2 and MGLUR3 knockout mice to explore in vivo receptor specificity of the MGLUR2/3 selective antagonist LY341495.Neuropharmacology. 2009 Aug;57(2):172-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.05.002. Epub 2009 May 27. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19477188
-
Contrasting effects of mu opioid receptor and delta opioid receptor deletion upon the behavioral and neurochemical effects of cocaine.Neuroscience. 2004;127(2):497-503. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.05.021. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15262338
-
Cocaine sensitization and craving: differing roles for dopamine and glutamate in the nucleus accumbens.J Addict Dis. 2001;20(3):43-54. doi: 10.1300/J069v20n03_05. J Addict Dis. 2001. PMID: 11681592 Review.
-
Role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the control of neuroendocrine function.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Sep;55(4):577-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.06.022. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18616955 Review.
Cited by
-
ADX106772, an mGlu2 receptor positive allosteric modulator, selectively attenuates oxycodone taking and seeking.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Nov 1;238:109666. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109666. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37463637 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of cocaine-induced conditioned locomotion is associated with altered expression of hippocampal glutamate receptors in mice lacking LPA1 receptors.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Mar;220(1):27-42. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2446-6. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 21887497
-
Comprehensive behavioral study of mGluR3 knockout mice: implication in schizophrenia related endophenotypes.Mol Brain. 2014 Apr 23;7:31. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-7-31. Mol Brain. 2014. PMID: 24758191 Free PMC article.
-
Using glutamate homeostasis as a target for treating addictive disorders.Behav Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;21(5-6):514-22. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32833d41b2. Behav Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20634691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of Type 2 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Decreases Sensitivity to Cocaine Reward in Rats.Cell Rep. 2017 Jul 11;20(2):319-332. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.046. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28700935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meldrum, B. S. (2000) J. Nutr. 130, 1007S–1015S. - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi, S. (1992) Science 258, 597–603. - PubMed
-
- Conn, P. J. & Pin, J. P. (1997) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 205–237. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl, R. (1999) Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 29, 83–120. - PubMed
-
- Schoepp, D. D. (2001) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299, 12–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

