DWI predicts future progression to Alzheimer disease in amnestic mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 15753434
- PMCID: PMC2771335
- DOI: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000153076.46126.E9
DWI predicts future progression to Alzheimer disease in amnestic mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
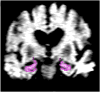
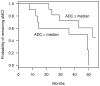
The authors assessed whether measures of hippocampal water diffusivity at baseline can predict future progression to Alzheimer disease (AD) in amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI). Higher baseline hippocampal diffusivity was associated with a greater risk of progression to AD in aMCI (p = 0.002). Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging may help identify patients with aMCI who will progress to AD as well as or better than structural MRI measures of hippocampal atrophy.
Figures


References
-
- Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rabins PV, Ritchie K, Rossor M, Thal L, Winblad B. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:1985–1992. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3. Washington, DC: 1987. DSM-III-R. revised.
-
- Mc Khann GM, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: report of the NINCDS ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–944. - PubMed
-
- Jack CR, Bentley MD, Twomey CK, Zinsmeister AR. MR imaging based volume measurements of the hippocampal formation and anterior temporal lobe: validation studies. Radiology. 1990;176:205–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
