Profile of soluble cytokine receptors in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 15753533
- PMCID: PMC1774443
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.043554
Profile of soluble cytokine receptors in Crohn's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Soluble cytokine receptors (sCRs) modulate the in vivo activity of cytokines. Deficient sCR production could participate in the pathogenesis and course of Crohn's disease (CD). The aim of the study was to examine the profile of sCRs in CD patients and their modulation by infliximab and corticosteroids.
Methods: We prospectively examined active CD patients (aCD) treated with either infliximab (n = 21) or corticosteroids (n = 9), CD patients in clinical remission (rCD, n = 20), ulcerative colitis patients (UC, n = 24), and healthy subjects (HS, n = 15). Cultures of colonic biopsies were also examined from CD inflamed (n = 8), CD non-inflamed (n = 7), and healthy mucosa (n = 8). Levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), soluble TNF receptor I (sTNFRI), soluble TNF receptor II (sTNFRII), interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), soluble IL-1 receptor I (sIL-1RI), soluble IL-1 receptor II (sIL-1RII), IL-6, soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and sgp130 were measured using ELISA.
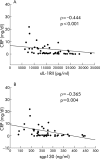
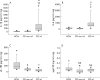
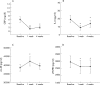
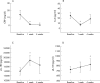
Results: Higher levels of sTNFRI (p<0.05, p<0.01), sTNFRII (p<0.01, p<0.01), sIL-1RI (p<0.05, NS), IL-6 (p<0.01, p<0.01), and sIL-6R (p<0.05, NS) were observed in aCD compared with rCD and HS. Interestingly, sIL-1RII (p<0.05, p<0.01) and sgp130 (p<0.01, p<0.01) were profoundly decreased in aCD compared with rCD and HS, and were negatively correlated with CRP. Deficient production of sIL-1RII was specific to CD (not observed in ulcerative colitis), and was further confirmed at the mucosal level. Infliximab decreased sTNFRII at one and four weeks (p<0.05) and enhanced sIL-6R levels at one week (p<0.05). Corticosteroids increased sIL-1RII levels at one week (p<0.05).
Conclusion: CD is associated with dysregulated production of sCRs. Deficiency in sIL-1RII and sgp130 may be essential to CD pathogenesis. Their replacement through the use of fusion proteins could represent future alternative therapeutic strategies for CD.
Figures
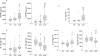

Similar articles
-
Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo.Nat Med. 2000 May;6(5):583-8. doi: 10.1038/75068. Nat Med. 2000. PMID: 10802717
-
High serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels are associated with lack of response to infliximab in fistulizing Crohn's disease.Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Sep;97(9):2350-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05990.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12358255
-
In vivo modulation of soluble "antagonistic" IL-6 receptor synthesis and release in ESRD.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Apr;16(4):1099-107. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004080628. Epub 2005 Feb 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 15716332
-
IL-6 transsignaling: the in vivo consequences.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005 May;25(5):241-53. doi: 10.1089/jir.2005.25.241. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005. PMID: 15871661 Review.
-
Adacolumn for selective leukocytapheresis as a non-pharmacological treatment for patients with disorders of the immune system: an adjunct or an alternative to drug therapy?J Clin Apher. 2005 Oct;20(3):171-84. doi: 10.1002/jca.20046. J Clin Apher. 2005. PMID: 15892107 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilization of physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model to assess disease-mediated therapeutic protein-disease-drug interaction in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Clin Transl Sci. 2022 Feb;15(2):464-476. doi: 10.1111/cts.13164. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Clin Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 34581012 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and drug target evaluation of 90 cardiovascular proteins in 30,931 individuals.Nat Metab. 2020 Oct;2(10):1135-1148. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00287-2. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Nat Metab. 2020. PMID: 33067605 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of colitis-associated cancer: natural compounds that target the IL-6 soluble receptor.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Dec;12(10):1221-38. doi: 10.2174/187152012803833080. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22583410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of inflammatory signals by cytokine-targeted therapies for inflammatory bowel diseases.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4):820-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01614.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21806600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor components sIL-6R and sgp130 as markers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018 Jul;33(7):927-936. doi: 10.1007/s00384-018-3069-8. Epub 2018 May 11. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018. PMID: 29748708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyajima A, Kitamura T, Harada N, et al. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol 1992;10:295–331. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Botran R, Chilton K, Ma Y. Soluble cytokine receptors: their roles in immunoregulation, disease and therapy. Adv Immunol 1996;63:269–336. - PubMed
-
- Mackiewicz A, Wiznerowicz M, Roeb E, et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor is biogically active in vivo. Cytokine 1995;7:142–9. - PubMed
-
- Narazaki M, Yasukawa K, Saito T, et al. Soluble forms of the interleukin-6 signal-transducing receptor component gp130 in human serum possessing a potential to inhibit signals through membrane-anchored gp130. Blood 1993;82:1120–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
