Proapoptotic and pronecrosis effect of different truncated hepatitis C virus core proteins
- PMID: 15754428
- PMCID: PMC1389739
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2005.B0295
Proapoptotic and pronecrosis effect of different truncated hepatitis C virus core proteins
Abstract
Objective: To study the roles of different truncated hepatitis C virus (HCV) core proteins (CORE) in the pathogenesis of HCV persistent infection and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to assess intracellular localization in transiently transfected cells.
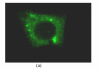
Methods: Seven truncated GFP (green fluorescent protein)-CORE fusion protein expression plasmids were constructed, which contained HCV CORE sequences derived from tumor tissues (BT) and non-tumor tissues (BNT) from one patient infected with HCV. Amino acid (aa) lengths were BT: 1-172 aa, 1-126 aa, 1-58 aa, 59-126 aa, 127-172 aa; BNT: 1-172 aa and C191: 1-172 aa respectively. Subcellular localization of CORE-GFP was analyzed by con-focal laser scanning microscope. Apoptosis and necrosis were quantified by flow cytometry.
Results: Different truncated CORE-GFP localized mainly in the cytoplasm, but nuclear staining was also observed. HCV CORE could induce apoptosis and necrosis, and different truncated COREs could induce cell apoptosis and necrosis at different levels. Among the same length 1-172 aa of BT, BNT and C191, the cell apoptosis and necrosis percentage of BT is highest, and C191 is the lowest (BT>BNT>C191). To the different fragment COREs of BT, N-terminal of CORE induced apoptosis and necrosis higher, compared with that of C-terminal (1-172 aa>1-126 aa>1-58 aa>127-172 aa>59-126 aa).
Conclusion: These results suggest HCV CORE could induce apoptosis and necrosis of cells, which might play an important role in the pathogenesis of HCV persistent infection and HCC and the different CORE domains of different HCV quasi-species might have some difference in their pathogenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Construction and expression of plasmids containing different truncated core proteins of hepatitis C virus derived from tumor and non-tumor tissues].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2004 Nov;12(11):643-7. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15623368 Chinese.
-
Morphological changes in intracellular lipid droplets induced by different hepatitis C virus genotype core sequences and relationship with steatosis.Hepatology. 2008 Jul;48(1):16-27. doi: 10.1002/hep.22288. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18570290
-
Cytoplasmic localization is important for transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B activation by hepatitis C virus core protein through its amino terminal region.Virology. 2001 Aug 1;286(2):391-402. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.0990. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11485407
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein: an update on its molecular biology, cellular functions and clinical implications.Med Princ Pract. 2006;15(6):405-16. doi: 10.1159/000095485. Med Princ Pract. 2006. PMID: 17047346 Review.
-
Dual behavior of HCV Core gene in regulation of apoptosis is important in progression of HCC.Infect Genet Evol. 2012 Mar;12(2):236-9. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Infect Genet Evol. 2012. PMID: 22266242 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of core gene of HCV 3a genotype using synthetic and vector derived siRNAs.Virol J. 2010 Nov 13;7:318. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-318. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 21073745 Free PMC article.
-
Charge neutralization as the major factor for the assembly of nucleocapsid-like particles from C-terminal truncated hepatitis C virus core protein.PeerJ. 2016 Nov 9;4:e2670. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2670. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27867765 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C viral heterogeneity based on core gene and an attempt to design small interfering RNA against strains resistant to interferon in rawalpindi, pakistan.Hepat Mon. 2012 Jun;12(6):398-407. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.6184. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Hepat Mon. 2012. PMID: 22879830 Free PMC article.
-
Associations among Genotype 1b Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein, Protein Kinase R, and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3.Hepat Mon. 2010 Fall;10(4):275-84. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Hepat Mon. 2010. PMID: 22312393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delhem N, Sabile A, Gajardo R, Podevin P, Abadie A, Balton MA, Kremsdorf D, Bretta L, Brechot C. Activation of the interferon-inducible protein kinase PKR by hepatocelluar carcinoma derived-hepatitis C virus CORE protein. Oncogene. 2000;20:5836–5845. - PubMed
-
- Francois C, Duverlie G, Rebouillat D, Khorsi H, Castelain S, Blum HE, Gatignol A, Wychowski C, Moradpour D, Meurs EF. Expression of hepatitis C virus proteins interferes with the antiviral action of interferon independently of PKR-mediated control of protein synthesis. J Virol. 2000;74:5587–5596. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hope RG, McLauchlan J. Sequence motifs required for lipid droplet association and protein stability are unique to the hepatitis C virus CORE protein. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:1913–1925. - PubMed
-
- Kountouras J, Zavos C, Chatzopoulos D. Apoptosis in hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2003;10(5):335–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

