Patient-reported outcome and quality of life instruments database (PROQOLID): frequently asked questions
- PMID: 15755325
- PMCID: PMC555954
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-3-12
Patient-reported outcome and quality of life instruments database (PROQOLID): frequently asked questions
Abstract
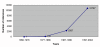
The exponential development of Patient-Reported Outcomes (PRO) measures in clinical research has led to the creation of the Patient-Reported Outcome and Quality of Life Instruments Database (PROQOLID) to facilitate the selection process of PRO measures in clinical research. The project was initiated by Mapi Research Trust in Lyon, France. Initially called QOLID (Quality of Life Instruments Database), the project's purpose was to provide all those involved in health care evaluation with a comprehensive and unique source of information on PRO and HRQOL measures available through the Internet.PROQOLID currently describes more than 470 PRO instruments in a structured format. It is available in two levels, non-subscribers and subscribers, at http://www.proqolid.org. The first level is free of charge and contains 14 categories of basic useful information on the instruments (e.g. author, objective, original language, list of existing translations, etc.). The second level provides significantly more information about the instruments. It includes review copies of over 350 original instruments, 120 user manuals and 350 translations. Most are available in PDF format. This level is only accessible to annual subscribers. PROQOLID is updated in close collaboration with the instruments' authors on a regular basis. Fifty or more new instruments are added to the database annually.Today, all of the major pharmaceutical companies, prestigious institutions (such as the FDA, the NIH's National Cancer Institute, the U.S. Veterans Administration), dozens of universities, public institutions and researchers subscribe to PROQOLID on a yearly basis. More than 800 users per day routinely visit the database.
Figures
References
-
- Acquadro C, Berzon R, Dubois D, Leidy NK, Marquis P, Revicki D, Rothman M, PRO Harmonization Group Incorporating the patient's perspective into drug development and communication: an ad hoc task force report of the Patient-reported Outcomes (PRO) Harmonization Group meeting at the Food and Drug Administration, February 16, 2001. Value Health. 2003;6:522–531. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4733.2003.65309.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The ERIQA Group Assessing Treatment Impact Using Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs): Challenges in Study Design, Conduct and Analysis. Meeting Report (Paris, May 10-11, 2004) Patient-Reported Outcomes Newsletter. 2005;3:1–16.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources