Complex tibial plateau fractures treated with Ilizarov external fixator with or without minimal internal fixation
- PMID: 15756605
- PMCID: PMC3456886
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-005-0638-6
Complex tibial plateau fractures treated with Ilizarov external fixator with or without minimal internal fixation
Abstract
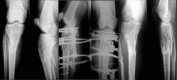
We treated 30 tibial plateau fractures (Schatzker Type VI) in 29 patients, with a mean age of 41.4 (20-76) years, with the Ilizarov fixator. In 18 fractures, we combined the treatment with minimal internal fixation. All fractures were the result of high-energy trauma, and 20 patients had associated injuries. Twenty-eight fractures were available for follow-up after 27 (16-36) months. Using The Knee Society clinical rating system, 18 knees were rated as excellent, seven as good, one as fair, and two as poor. There was a direct correlation between the presence of associated injuries and the final outcome. The most significant concomitant injuries were distal femoral fractures and extensive soft-tissue injury. This study emphasizes the clinical success and low morbidity associated with the use of external fixation and minimal internal fixation.
Nous avons traité chirurgicalement 30 fractures du plateau tibial (Type Schatzker VI) chez 29 malades—âge moyen de 41,4 ans (20–76)—avec un fixateur d’Ilizarov. Pour 18 fractures nous avons combiné le traitement avec une fixation interne légère. Toutes les fractures étaient le résultat d’un traumatisme à haute énergie et 20 patients avaient des lésions associées. Après un suivi de 27 mois (16–36) 28 fractures étaient étudiables. Avec le score de la Knee Society, 18 genoux ont été estimés comme excellents, sept comme bons, un comme moyen, et deux comme mauvais. Il y avait une corrélation directe entre la présence de blessures associées et le dernier résultat, le plus significatif étant l’existence d’une fracture fémorale distale et l’importance des lésions des parties molles. L’étude met en relief le succès clinique et la basse morbidité associés à l’usage du fixateur externe et de la fixation interne légère.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Comparative study on internal fixation and external fixation for the treatment of complex tibial plateau fracture].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Aug;22(8):952-5. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18773812 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Compartment syndrome in Schatzker type VI plateau fractures and medial condylar fracture-dislocations treated with temporary external fixation.J Orthop Trauma. 2009 Aug;23(7):502-6. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181a18235. J Orthop Trauma. 2009. PMID: 19633459
-
Treatment of fractures of the tibial plateau (Schatzker VI) with external fixators versus plate osteosynthesis.Injury. 2018 Nov;49 Suppl 3:S12-S18. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.09.059. Injury. 2018. PMID: 30415663
-
High-energy fractures of the tibial plateau.Orthop Clin North Am. 1994 Oct;25(4):723-52. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994. PMID: 8090483 Review.
-
Open grade III "floating ankle" injuries: a report of eight cases with review of literature.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007 Oct;127(8):625-31. doi: 10.1007/s00402-007-0314-y. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007. PMID: 17410371 Review.
Cited by
-
Results of ring (Ilizarov) fixator in high energy Schatzker type VI fractures of proximal tibia.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018 Apr-Jun;9(2):186-191. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018. PMID: 29896026 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes Between Open Reduction and Internal Fixation and Ilizarov for Schatzker Type V and Type VI Fractures.Cureus. 2019 Jun 14;11(6):e4902. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4902. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31417831 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical Analysis of the Behaviour at the Metaphyseal-Diaphyseal Junction of Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures Using Two Circular Fixator Configurations.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2020 Sep-Dec;15(3):138-145. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10080-1507. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2020. PMID: 34025793 Free PMC article.
-
Midterm Results of a Combined Biological and Mechanical Approach for the Treatment of a Complex Knee Lesion.Cartilage. 2012 Jul;3(3):288-92. doi: 10.1177/1947603512436371. Cartilage. 2012. PMID: 26069639 Free PMC article.
-
Ilizarov Ring External Fixation for Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021 Nov 11;57(4):667-674. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1739171. eCollection 2022 Aug. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 35966423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballmer FT, Hertel R, Notzli HP. Treatment of tibial plateau fractures with small fragment internal fixation: a preliminary report. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14:467–474. - PubMed
-
- Buckle R, Blake R, Watson JT, et al. Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures with the Ilizarov external fixator. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7:167.
-
- Collinge C, Sanders R, DiPasquale T. Treatment of complex tibial periarticular fractures using percutaneous techniques. Clin Ortop. 2000;375:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Dendrinos GK, Kontos S, Katsenis D, Dalas A. Treatment of high-energy tibial plateau fractures by the Ilizarov circular fixator. J Bone Joint Surg Br . 1996;78:710–717. - PubMed
-
- Guadinez RF, Mallik AR, Sporn M. Hybrid external fixation of comminuted tibial plateau fractures. Clin Ortop. 1996;328:203–210. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

