Changes of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity during treatment of patients with Graves' disease
- PMID: 15759385
- PMCID: PMC4534898
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1986.1.1.104
Changes of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity during treatment of patients with Graves' disease
Abstract
Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity was measured spectrophotometrically, and serum thyrotropin-binding-inhibitory immunoglobulin (TBII) activity was measured by radioreceptor assay in normal subjects and in patients with Graves’ disease serially before and during treatment, and these activities were compared with each other and with thyroid hormone levels in various thyroid functional status. Correlation between serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity and serum thyroid hormone level was pursued with relation to the changes of thyroid functional status in patients with Graves’ disease during treatment.
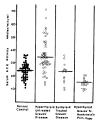
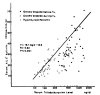
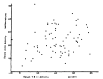
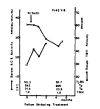
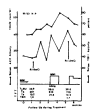
Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity was significantly elevated in patients with hyperthyroid Graves’ disease before the start of treatment (35 ± 13 nmol/min/ml, n=50), and not in patients with Graves’ disease, euthyroid state during treatment with antithyroid drugs or radioactive iodine (23 ± 9 nmol/min/ml, n=12), but decreased significantly in patients with Graves’ disease, hypothyroid state transiently during treatment (15 ± 4 nmol/min/ml, n=12), respectively in comparison with normal control subjects. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity was positively correlated with the log value of serum T3 concentration (r=0.62, p<0.001, n=95), and with the log value of free thyroxine index (r=0.66, p<0.001, n=91) but not statistically significantly with serum TBII activity. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity was followed in 11 patients with initially increased activity and the activity decreased in proportion to serum thyroid hormone level during treatment, irrespective of treatment modality. It is suggested that thyroid hormones play a role in the increase and decrease of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity directly or indirectly influencing the peripheral tissues (probably reticuloendothelial cells or peripheral endothelial cells) in patients with Graves’ disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Thyroid-stimulating antibody is related to Graves' ophthalmopathy, but thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin is related to hyperthyroidism in patients with Graves' disease.Thyroid. 2000 Sep;10(9):809-13. doi: 10.1089/thy.2000.10.809. Thyroid. 2000. PMID: 11041459
-
Graves' ophthalmopathy in the absence of elevated free thyroxine and triiodothyronine levels: prevalence, natural history, and thyrotropin receptor antibody levels.Thyroid. 2000 Dec;10(12):1093-100. doi: 10.1089/thy.2000.10.1093. Thyroid. 2000. PMID: 11201855
-
Effect of 1 alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3 on serum levels of thyroid hormones in hyperthyroid patients with untreated Graves' disease.Metabolism. 1997 Oct;46(10):1184-8. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90214-6. Metabolism. 1997. PMID: 9322804 Clinical Trial.
-
Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) in Graves' disease.Endocr J. 1998 Dec;45(6):701-8. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.45.701. Endocr J. 1998. PMID: 10395224 Review. No abstract available.
-
The role of stimulating, function-blocking and growth-blocking anti-TSH receptor antibodies (TRAbs) in GD, Hashimoto's disease and in atrophic thyroiditis.Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2003 Feb;64(1):31-6. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12707631 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Prospective role of thyroid disorders in monitoring COVID-19 pandemic.Heliyon. 2020 Dec;6(12):e05712. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05712. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33344794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement in Blood Pressure After Intermittent Fasting in Hipertension: Could Renin-Angiotensin System and Autonomic Nervous System Have a Role?Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Mar;120(5):e20220756. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220756. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37098959 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
A framework for exclusion of alternative diagnoses in sarcoidosis.J Autoimmun. 2024 Dec;149:103288. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2024.103288. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Autoimmun. 2024. PMID: 39084998 Review.
References
-
- Nakamura Y, Takedo M, et al. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in patients with Graves’ disease and hypothyroidism. Igaku-no-Ayumi. 1980;113:27.
-
- Yotsumoto H, Imai Y, Kuzuya N, Uchimura H, Matsuzaki F. Increased levels of serum angiotensin-converting activity in hyperthyroidism. Am J Med. 1983;75:233. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Takeda T, Ishii M, Nishiyama K, Yamakada M, Hirata Y, Kimura K, Murao S. Elevation of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in patients with hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endo Meta. 1982;55:931. - PubMed
-
- Silverstein E, Schussler GC, Friedlang J. Elevated serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in hyperthyroidism. Am J Med. 1983;75:233. - PubMed
-
- Friedland J, Setton C, Silverstein E. Angiotensin converting enzyme, induction by steroids in rabbit alveolar macrophages in culture. Science. 1977;197:64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
