Suppression of NF-kappaB-mediated beta-defensin gene expression in the mammalian airway by the Bordetella type III secretion system
- PMID: 15760449
- PMCID: PMC2111170
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00473.x
Suppression of NF-kappaB-mediated beta-defensin gene expression in the mammalian airway by the Bordetella type III secretion system
Abstract
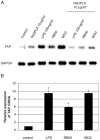
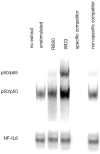
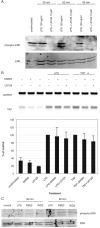
Expression of innate immune genes such as beta-defensins is induced in airway epithelium by bacterial components via activation of NF-kappaB. We show here that live Gram-negative bacteria can similarly stimulate this pathway, resulting in upregulation of the beta-defensin tracheal antimicrobial peptide (TAP) in primary cultures of bovine tracheal epithelial cells (TECs), by a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated pathway. The Gram-negative airway pathogen Bordetella bronchiseptica possesses a type III secretion system previously suggested to inhibit the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB in a cell line by immunohistochemistry. We therefore hypothesized that this pathogen might interfere in the innate immune response of the epithelium. Exposure of TECs to wild-type B. bronchiseptica suppressed the activation of NF-kappaB and the subsequent induction of TAP mRNA levels, whereas a type III secretion-defective strain did not. These results suggest a mechanism for bacterial evasion of the innate immune response in the airway, which could allow for the observed persistent colonization of this pathogen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of host immune responses, induction of apoptosis and inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by the Bordetella type III secretion system.Mol Microbiol. 2000 Mar;35(5):991-1004. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01785.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10712682
-
Regulation of tracheal antimicrobial peptide gene expression in airway epithelial cells of cattle.Vet Res. 2016 Mar 17;47:44. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0329-x. Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 26987959 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4-dependent early elicited tumor necrosis factor alpha expression is critical for innate host defense against Bordetella bronchiseptica.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6650-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6650-6658.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501798 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of beta-defensin gene expression in tracheal epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2000 Jan;68(1):113-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.113-119.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10603376 Free PMC article.
-
Host defense peptides in the oral cavity and the lung: similarities and differences.J Dent Res. 2008 Oct;87(10):915-27. doi: 10.1177/154405910808701011. J Dent Res. 2008. PMID: 18809744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The host defense peptide beta-defensin 1 confers protection against Bordetella pertussis in newborn piglets.Infect Immun. 2006 Apr;74(4):2338-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.4.2338-2352.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16552064 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the NF-kappaB pathway by Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin.PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003825. Epub 2008 Nov 27. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 19043589 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of type III secretion and virulence genes in Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica by a secreted anti-σ factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 1;113(9):2341-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600320113. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26884180 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of NF-κB signalling by microbial pathogens.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Apr;9(4):291-306. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2539. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21383764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of human beta-defensin-1 (hBD-1) in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDC), monocytes, and epithelial cells by influenza virus, Herpes simplex virus, and Sendai virus and its possible role in innate immunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2011 Aug;90(2):343-56. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0209079. Epub 2011 May 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21551252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker MN, Diamond G, Verghese MW, Randell SH. CD14-dependent lipopolysaccharide-induced beta-defensin-2 expression in human tracheobronchial epithelium. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:29731–29736. - PubMed
-
- Cotter PA, Miller JF. A mutation in the Bordetella bronchiseptica bvgS gene results in reduced virulence and increased resistance to starvation, and identifies a new class of Bvg-regulated antigens. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:671–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

