A two year randomised controlled trial of intramuscular depot steroids in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis who have shown an incomplete response to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs
- PMID: 15760929
- PMCID: PMC1755652
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.030908
A two year randomised controlled trial of intramuscular depot steroids in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis who have shown an incomplete response to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs
Abstract
Background: In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), intramuscular (IM) pulsed depomedrone expedites an immediate response to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Although IM depomedrone is also widely used to treat disease flares in patients treated with DMARDs, its effect on radiological progression has not been assessed.
Objective: To evaluate the benefits of 120 mg IM depomedrone versus placebo in patients with established RA whose disease was inadequately controlled by existing DMARDs.
Methods: In a 2 year prospective randomised controlled trial patients were assessed using the ILAR/WHO core dataset, disease activity score (DAS28), x ray examination of hands and feet scored by Larsen's method, and bone densitometry.
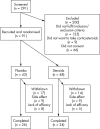
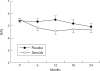
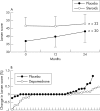
Results: 291 patients with RA were screened, 166 were eligible, and 91 consented and were randomised. Disease activity improved more rapidly in the steroid treated patients than with placebo, but after 6 months no difference remained. A small but significant reduction in erosive damage in the steroid group compared with placebo was also found. More adverse reactions occurred in the steroid treated group than in the placebo patients (55 v 42), especially those reactions traditionally related to steroids (16 v 2), including vertebral fracture, diabetes, and myocardial infarction. Hip bone density fell significantly in steroid treated but not placebo patients.
Conclusions: IM depomedrone improved disease activity in the short term and produced a small reduction in bone erosion at the cost of a significant increase in adverse events. Despite the initial benefit of IM depomedrone, when patients respond suboptimally to a DMARD they should not be given long term additional steroids but should be treated with alternative or additional DMARDs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

