Ca2+ permeability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors from rat dorsal root ganglion neurones
- PMID: 15760934
- PMCID: PMC1464485
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.084871
Ca2+ permeability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors from rat dorsal root ganglion neurones
Abstract
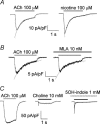
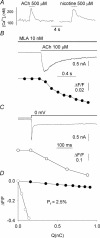
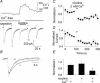
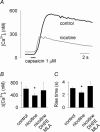
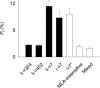
Ca2+ entry through neuronal nicotinic ACh receptors (nAChRs) modulates many biological processes in nervous tissue. In order to study the functional role of nAChRs in peripheral sensory signalling, we measured their Ca2+ permeability in rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurones, and analysed the effects of nAChR-mediated Ca2+ influx on the function of the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. The fractional Ca2+ current (P(f), i.e. the percentage of current carried by Ca2+ ions) flowing through nAChR channels was measured by Ca2+ imaging fluorescence microscopy in combination with the patch-clamp technique. Functional nAChRs were expressed in a subset of adult DRG neurones (about 24% of the cells), typically with small to medium size as measured by their capacitance (40 +/- 3 pF). In most cells, ACh evoked slowly desensitizing currents, insensitive to methyllycaconitine (MLA, 10 nm), a potent antagonist of homomeric nAChRs. Fast decaying currents, probably mediated by alpha7*-nAChRs (i.e. native alpha7-containing nAChRs), were observed in 15% of ACh-responsive cells, in which slowly decaying currents, mediated by heteromeric nAChRs, were simultaneously present. The nAChRs of adult DRG neurones exhibited a P(f) value of 2.2 +/- 0.6% in the presence of MLA and 1.9 +/- 0.6% (P > 0.1) in the absence of MLA, indicating that homomeric MLA-sensitive nAChRs do not contribute to Ca2+ entry into adult DRG neurones. Conversely, 10% of neonatal DRG neurones showed ACh-evoked currents completely blocked by MLA. In these neurones, nAChRs showed a larger P(f) value (9.5 +/- 1.5%), indicating the expression of bona fide alpha7*-nAChRs. Finally, we report that Ca2+ influx through nAChRs in adult DRG neurones negatively modulated the TRPV1-mediated responses, representing a possible mechanism underlying the analgesic properties of nicotinic agonists on sensory neurones.
Figures

References
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Cortes WS, Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Choline is a selective agonist of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the rat brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1997;12:2734–2742. - PubMed
-
- Brioni JD, Decker MW, Sullivan JP, Arneric SP. The pharmacology of (–)-nicotine and novel cholinergic channel modulators. Adv Pharmacol. 1997;37:153–214. - PubMed
-
- Caggiula AR, Epstein LH, Perkins KA, Saylor S. Different methods of assessing nicotine-induced antinociception may engage different neural mechanisms. Psychopharmacology. 1995;122:301–306. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Julius D. The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:487–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

