Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis
- PMID: 15761492
- PMCID: PMC1059449
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23273
Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis
Abstract
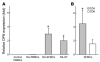
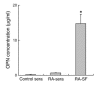
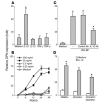
Osteopontin (OPN) is an extracellular matrix protein of pleiotropic properties and has been recently recognized as a potential inflammatory cytokine. In this study, we demonstrate, for the first time to our knowledge, that overexpression of OPN in synovial T cells is associated with local inflammatory milieu and that OPN acts as an important mediator in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. The study revealed that mRNA expression of OPN was highly elevated in CD4(+) synovial T cells derived from patients with RA, which correlated with increased OPN concentrations in synovial fluid (SF). The pattern of OPN overexpression was confined to rheumatoid synovium and correlated with coexpression of selected OPN receptors in synovial T cells, including integrins alphav and beta1 and CD44. RA-derived SF stimulated the expression of OPN in T cells, which was attributable to IL-10 present in SF and abrogated by anti-IL-10 antibody. Among the more than 300 autoimmune and inflammatory response genes examined, OPN selectively induced the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines known to promote migration and recruitment of inflammatory cells. Furthermore, it was evident that OPN activated transcription factor NF-kappaB in mononuclear cells. The study has important implications for understanding the role of OPN in rheumatoid synovitis and other inflammatory conditions.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Overexpression of osteopontin in rheumatoid synovial mononuclear cells is associated with joint inflammation, not with genetic polymorphism.J Rheumatol. 2005 Mar;32(3):410-6. J Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 15742430
-
Role of osteopontin in induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and macrophage inflammatory protein 1beta through the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jul;60(7):1957-65. doi: 10.1002/art.24625. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19565503
-
Interleukin-21 induces T-cell activation and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis.Scand J Immunol. 2006 Nov;64(5):515-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2006.01795.x. Scand J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17032244
-
The role of Osteopontin in tumor metastasis.J Surg Res. 2004 Oct;121(2):228-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2004.03.028. J Surg Res. 2004. PMID: 15501463 Review.
-
Synovial fluid estrogens in rheumatoid arthritis.Autoimmun Rev. 2004 Mar;3(3):193-8. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2003.08.003. Autoimmun Rev. 2004. PMID: 15110231 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20, a potential biomarker for Graves' disease, is regulated by osteopontin.PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e64277. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064277. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717583 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization of osteopontin inhibits obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.Diabetes. 2010 Apr;59(4):935-46. doi: 10.2337/db09-0404. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20107108 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin mediates Citrobacter rodentium-induced colonic epithelial cell hyperplasia and attaching-effacing lesions.Am J Pathol. 2010 Sep;177(3):1320-32. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091068. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20651246 Free PMC article.
-
The rs3768777-G allele of ITGAV gene is associated with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2014 May;34(5):693-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2925-7. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Rheumatol Int. 2014. PMID: 24375314
-
Intranasal Delivery of RGD Motif-Containing Osteopontin Icosamer Confers Neuroprotection in the Postischemic Brain via αvβ3 Integrin Binding.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;53(8):5652-63. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9480-z. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26482372
References
-
- Pope RM, Pahlavani MA, Lacour E, Sambol S, Desai BV. Antigen specificity of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32:1371–1380. - PubMed
-
- Devereux D, O’Hehir RE, McGuire J, van Schooten WC, Lamb JR. HLA-DR4Dw4-restricted T cell recognition of self antigen(s) in the rheumatoid synovial compartment. Int. Immunol. 1991;3:635–640. - PubMed
-
- Res PC, et al. Inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis contain T cells that display in vitro proliferation to antigens present in autologous synovial fluid. Function analysis on the basis of synovial-fluid-reactive T cell clones and lines. Hum. Immunol. 1994;40:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

