The MODY1 gene HNF-4alpha regulates selected genes involved in insulin secretion
- PMID: 15761495
- PMCID: PMC1059446
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI22365
The MODY1 gene HNF-4alpha regulates selected genes involved in insulin secretion
Abstract
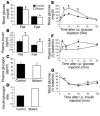
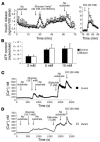
Mutations in the gene encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha (HNF-4alpha) result in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). To determine the contribution of HNF-4alpha to the maintenance of glucose homeostasis by the beta cell in vivo, we derived a conditional knockout of HNF-4alpha using the Cre-loxP system. Surprisingly, deletion of HNF-4alpha in beta cells resulted in hyperinsulinemia in fasted and fed mice but paradoxically also in impaired glucose tolerance. Islet perifusion and calcium-imaging studies showed abnormal responses of the mutant beta cells to stimulation by glucose and sulfonylureas. These phenotypes can be explained in part by a 60% reduction in expression of the potassium channel subunit Kir6.2. We demonstrate using cotransfection assays that the Kir6.2 gene is a transcriptional target of HNF-4alpha. Our data provide genetic evidence that HNF-4alpha is required in the pancreatic beta cell for regulation of the pathway of insulin secretion dependent on the ATP-dependent potassium channel.
Figures



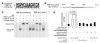
Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha is essential for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by pancreatic beta-cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 24;281(8):5246-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507496200. Epub 2005 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16377800
-
Genetic evidence that HNF-1alpha-dependent transcriptional control of HNF-4alpha is essential for human pancreatic beta cell function.J Clin Invest. 2002 Sep;110(6):827-33. doi: 10.1172/JCI15085. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12235114 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha involved in type 1 maturity-onset diabetes of the young is a novel target of AMP-activated protein kinase.Diabetes. 2001 Jul;50(7):1515-21. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.7.1515. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11423471
-
HNF-4alpha: from MODY to late-onset type 2 diabetes.Trends Mol Med. 2004 Nov;10(11):521-4. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.004. Trends Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15519277 Review.
-
Different genes, different diabetes: lessons from maturity-onset diabetes of the young.Ann Med. 2002;34(3):207-16. Ann Med. 2002. PMID: 12173691 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Go Diabetic: A Glimpse on Monogenic Variants.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 17;12:648284. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.648284. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34079523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticosteroid-induced bradycardia in multiple sclerosis and maturity-onset diabetes of the young due to hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha mutation: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jul 26;10(21):7415-7421. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7415. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36158012 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α initiates cell cycle entry, but is not sufficient to promote β-cell expansion in human islets.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Sep;26(9):1590-602. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1019. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22798294 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic Analyses of miRNA-mRNA Signature during hiPSC Differentiation towards Insulin-Producing Cells upon HNF4α Mutation.Biomedicines. 2020 Jun 27;8(7):179. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8070179. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32605028 Free PMC article.
-
HNF4A defines tissue-specific circadian rhythms by beaconing BMAL1::CLOCK chromatin binding and shaping the rhythmic chromatin landscape.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 3;12(1):6350. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26567-3. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34732735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shih DQ, Stoffel M. Molecular etiologies of MODY and other early-onset forms of diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2002;2:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Yamagata K, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3) Nature. 1996;384:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Gragnoli C, et al. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young due to a mutation in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha binding site in the promoter of the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha gene. Diabetes. 1997;46:1648–1651. - PubMed
-
- Silander K, et al. Genetic variation near the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha gene predicts susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53:1141–1149. - PubMed
-
- Love-Gregory LD, et al. A common polymorphism in the upstream promoter region of the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha gene on chromosome 20q is associated with type 2 diabetes and appears to contribute to the evidence for linkage in an ashkenazi jewish population. Diabetes. 2004;53:1134–1140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK056947/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK061226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK60064/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56947/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK55743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK50306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK056947/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK55342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK61226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK19525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060064/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

