Dimerization of MLL fusion proteins and FLT3 activation synergize to induce multiple-lineage leukemogenesis
- PMID: 15761502
- PMCID: PMC1062890
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI22725
Dimerization of MLL fusion proteins and FLT3 activation synergize to induce multiple-lineage leukemogenesis
Abstract
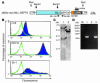
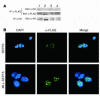
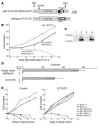
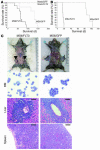
The mechanisms by which mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) fusion products resulting from in utero translocations in 11q23 contribute to leukemogenesis and infant acute leukemia remain elusive. It is still controversial whether the MLL fusion protein is sufficient to induce acute leukemia without additional genetic alterations, although carcinogenesis in general is known to result from more than 1 genetic disorder accumulating during a lifetime. Here we demonstrate that the fusion partner-mediated homo-oligomerization of MLL-SEPT6 is essential to immortalize hematopoietic progenitors in vitro. MLL-SEPT6 induced myeloproliferative disease with long latency in mice, but not acute leukemia, implying that secondary genotoxic events are required to develop leukemia. We developed in vitro and in vivo model systems of leukemogenesis by MLL fusion proteins, where activated FMS-like receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) together with MLL-SEPT6 not only transformed hematopoietic progenitors in vitro but also induced acute biphenotypic or myeloid leukemia with short latency in vivo. In these systems, MLL-ENL, another type of the fusion product that seems to act as a monomer, also induced the transformation in vitro and leukemogenesis in vivo in concert with activated FLT3. These findings show direct evidence for a multistep leukemogenesis mediated by MLL fusion proteins and may be applicable to development of direct MLL fusion-targeted therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disruption of Sept6, a fusion partner gene of MLL, does not affect ontogeny, leukemogenesis induced by MLL-SEPT6, or phenotype induced by the loss of Sept4.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(24):10965-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10965-10978.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16314519 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of leukemogenesis mediated by MLL fusion proteins.Oncogene. 2001 Sep 10;20(40):5695-707. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204639. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11607819 Review.
-
The small oligomerization domain of gephyrin converts MLL to an oncogene.Blood. 2004 May 15;103(10):3876-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-11-3817. Epub 2004 Jan 29. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14751928
-
Structure of AF3p21, a new member of mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) fusion partner proteins-implication for MLL-induced leukemogenesis.Leuk Lymphoma. 2001 Aug;42(4):595-602. doi: 10.3109/10428190109099319. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001. PMID: 11697487 Review.
-
Tet1 is not required for myeloid leukemogenesis by MLL-ENL in novel mouse models.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 11;16(3):e0248425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248425. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33705482 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Disruption of Sept6, a fusion partner gene of MLL, does not affect ontogeny, leukemogenesis induced by MLL-SEPT6, or phenotype induced by the loss of Sept4.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(24):10965-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10965-10978.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16314519 Free PMC article.
-
MLL-AF9 and FLT3 cooperation in acute myelogenous leukemia: development of a model for rapid therapeutic assessment.Leukemia. 2008 Jan;22(1):66-77. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404951. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Leukemia. 2008. PMID: 17851551 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-125b-1 accelerates a C-terminal mutant of C/EBPα (C/EBPα-C(m))-induced myeloid leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2012 Sep;96(3):334-41. doi: 10.1007/s12185-012-1143-5. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Int J Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22843432
-
MLL fusions: pathways to leukemia.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jul;8(13):1204-11. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.13.8924. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19729989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knock-in of an internal tandem duplication mutation into murine FLT3 confers myeloproliferative disease in a mouse model.Blood. 2008 Apr 1;111(7):3849-58. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-109942. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18245664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Look AT. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science. 1997;278:1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Rowley JD. The critical role of chromosome translocations in human leukemias. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1998;32:495–519. - PubMed
-
- Tkachuk DC, Kohler S, Cleary ML. Involvement of a homolog of Drosophila trithorax by 11q23 chromosomal translocations in acute leukemias. Cell. 1992;71:691–700. - PubMed
-
- Gu Y, et al. The t(4;11) chromosome translocation of human acute leukemias fuses the ALL-1 gene, related to Drosophila trithorax, to the AF-4 gene. Cell. 1992;71:701–708. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi Y. The molecular genetics of recurring chromosome abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia. Semin. Hematol. 2000;37:368–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

