Differential labeling of myosin V heads with quantum dots allows direct visualization of hand-over-hand processivity
- PMID: 15764654
- PMCID: PMC1305523
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.061903
Differential labeling of myosin V heads with quantum dots allows direct visualization of hand-over-hand processivity
Abstract
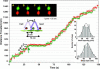
The double-headed myosin V molecular motor carries intracellular cargo processively along actin tracks in a hand-over-hand manner. To test this hypothesis at the molecular level, we observed single myosin V molecules that were differentially labeled with quantum dots having different emission spectra so that the position of each head could be identified with approximately 6-nm resolution in a total internal reflectance microscope. With this approach, the individual heads of a single myosin V molecule were observed taking 72-nm steps as they alternated positions on the actin filament during processive movement. In addition, the heads were separated by 36 nm during pauses in motion, suggesting attachment to actin along its helical repeat. The 36-nm interhead spacing, the 72-nm step size, and the observation that heads alternate between leading and trailing positions on actin are obvious predictions of the hand-over-hand model, thus confirming myosin V's mode of walking along an actin filament.
Figures
References
-
- Forkey, J. N., M. E. Quinlan, M. A. Shaw, J. E. Corrie, and Y. E. Goldman. 2003. Three-dimensional structural dynamics of myosin V by single-molecule fluorescence polarization. Nature. 422:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Yildiz, A., J. N. Forkey, S. A. McKinney, T. Ha, Y. E. Goldman, and P. R. Selvin. 2003. Myosin V walks hand-over-hand: single fluorophore imaging with 1.5-nm localization. Science. 300:2061–2065. - PubMed
-
- Walker, M. L., S. A. Burgess, J. R. Sellers, F. Wang, J. A. Hammer, III, J. Trinick, and P. J. Knight. 2000. Two-headed binding of a processive myosin to F-actin. Nature. 405:804–807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

