Hypocapnic but not metabolic alkalosis impairs alveolar fluid reabsorption
- PMID: 15764729
- PMCID: PMC2718461
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200408-998OC
Hypocapnic but not metabolic alkalosis impairs alveolar fluid reabsorption
Abstract
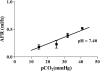
Acid-base disturbances, such as metabolic or respiratory alkalosis, are relatively common in critically ill patients. We examined the effects of alkalosis (hypocapnic or metabolic alkalosis) on alveolar fluid reabsorption in the isolated and continuously perfused rat lung model. We found that alveolar fluid reabsorption after 1 hour was impaired by low levels of CO2 partial pressure (PCO2; 10 and 20 mm Hg) independent of pH levels (7.7 or 7.4). In addition, PCO2 higher than 30 mm Hg or metabolic alkalosis did not have an effect on this process. The hypocapnia-mediated decrease of alveolar fluid reabsorption was associated with decreased Na,K-ATPase activity and protein abundance at the basolateral membranes of distal airspaces. The effect of low PCO2 on alveolar fluid reabsorption was reversible because clearance normalized after correcting the PCO2 back to normal levels. These data suggest that hypocapnic but not metabolic alkalosis impairs alveolar fluid reabsorption. Conceivably, correction of hypocapnic alkalosis in critically ill patients may contribute to the normalization of lung ability to clear edema.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypocapnia-induced ventilation/perfusion mismatch: a direct CO2 or pH-mediated effect?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Nov;152(5 Pt 1):1534-9. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.5.7582289. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. PMID: 7582289
-
Proximal tubular bicarbonate reabsorption and PCO2 in chronic metabolic alkalosis in the rat.J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1385-95. doi: 10.1172/JCI111095. J Clin Invest. 1983. PMID: 6415109 Free PMC article.
-
Leukotriene D4 activates alveolar epithelial Na,K-ATPase and increases alveolar fluid clearance.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004 Feb 1;169(3):407-12. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200304-472OC. Epub 2003 Oct 24. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 14578215
-
Simple acid-base disorders.Am J Hosp Pharm. 1985 Sep;42(9):1992-2004. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1985. PMID: 3931455 Review.
-
Regulation of lung edema clearance by dopamine.Isr Med Assoc J. 2003 Jan;5(1):47-50. Isr Med Assoc J. 2003. PMID: 12592959 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of ventilation pressure on alveolar fluid clearance and beta-agonist responses in mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Oct;297(4):L785-93. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00096.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19684202 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytosis in the adaptation to cellular stress.Cell Stress. 2020 Aug 18;4(10):230-247. doi: 10.15698/cst2020.10.232. Cell Stress. 2020. PMID: 33024932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alveolar fluid clearance in acute lung injury: what have we learned from animal models and clinical studies?Intensive Care Med. 2007 Jul;33(7):1229-1240. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0662-7. Epub 2007 May 25. Intensive Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17525842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin regulates alveolar epithelial function by inducing Na+/K+-ATPase translocation to the plasma membrane in a process mediated by the action of Akt.J Cell Sci. 2010 Apr 15;123(Pt 8):1343-51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.066464. Epub 2010 Mar 23. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20332111 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates ventilator-induced lung injury.Crit Care. 2010;14(6):R234. doi: 10.1186/cc9389. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 21184683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rutschman DH, Olivera W, Sznajder JI. Active transport and passive liquid movement in isolated perfused rat lungs. J Appl Physiol 1993;75:1574–1580. - PubMed
-
- Saumon G, Basset G. Electrolyte and fluid transport across the mature alveolar epithelium. J Appl Physiol 1993;74:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Sznajder JI, Olivera WG, Ridge KM, Rutschman DH. Mechanisms of lung liquid clearance during hyperoxia in isolated rat lungs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995;151:1519–1525. - PubMed
-
- Sznajder JI, Factor P, Ingbar DH. Lung edema clearance: role of Na+-K+-ATPase. J Appl Physiol 2002;93:1860–1866. - PubMed
-
- Dada LA, Sznajder JI. Mechanisms of pulmonary edema clearance during acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: Role of the Na,K-ATPase. Crit Care Med 2003;31:248–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

