Regulation of the muscarinic K+ channel by extracellular ATP through membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in guinea-pig atrial myocytes
- PMID: 15765102
- PMCID: PMC1576138
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706191
Regulation of the muscarinic K+ channel by extracellular ATP through membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in guinea-pig atrial myocytes
Abstract
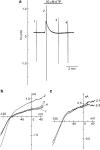
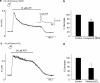
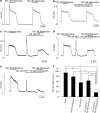
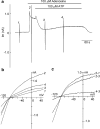
1 The present study was designed to examine the functional role of membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P(2)) in the regulation of the muscarinic K(+) channel (I(K,ACh)) by extracellular ATP and adenosine in guinea-pig atrial myocytes, using the whole-cell patch-clamp method. 2 Bath application of ATP in micromolar concentrations typically evoked a transient activation of I(K,ACh); a rapid activation phase was consistently followed by a progressive decline even to the baseline level despite the continued presence of ATP. This progressive decline of I(K,ACh) was significantly attenuated either by blockade of phospholipase C (PLC) with compound 48/80 (100 microM) or by addition of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) (50 microM) to the cell inside, suggesting that depletion of membrane PtdIns(4,5)P(2) via PLC activation is mainly, if not totally, responsible for the progressive decline of I(K,ACh) during the presence of ATP. 3 When atrial myocytes were exposed to wortmannin (50 microM) following ATP (50 microM) application to impair the resynthesis of PtdIns(4,5)P(2), the activation of I(K,ACh) evoked by subsequently applied ATP (50 microM) was greatly reduced. Activation of I(K,ACh) by adenosine (100 microM) was partially reduced by pretreatment of atrial myocytes with ATP (100 microM) and was largely abolished by a further addition of wortmannin (50 microM) in the presence of ATP (100 microM). These results support the view that the activation of I(K,ACh) by ATP and adenosine depends on membrane PtdIns(4,5)P(2) that is subject to reduction by extracellular ATP. 4 The present study thus provides functional evidence to suggest that extracellular ATP activates PLC and thereby depletes membrane PtdIns(4,5)P(2) that is critically involved in the activation process of I(K,ACh) by its agonists ATP and adenosine in guinea-pig atrial myocytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of cardiac IKs potassium current by membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 3;279(49):50726-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409374200. Epub 2004 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15364935
-
Effects of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs on the acetylcholine receptor-operated potassium current in guinea pig atrial myocytes.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004 Nov;95(5):234-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2004.pto950506.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 15546478
-
Modulation of the muscarinic K+ channel by P2-purinoceptors in guinea-pig atrial myocytes.J Physiol. 1996 Dec 1;497 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):379-93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021775. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8961182 Free PMC article.
-
M current mystery messenger revealed?Neuron. 2002 Aug 1;35(3):411-2. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00792-4. Neuron. 2002. PMID: 12165463 Review.
-
K(ATP) channels: linker between phospholipid metabolism and excitability.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Sep 15;60(6):735-40. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00267-7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10930527 Review.
Cited by
-
A long QT mutation substitutes cholesterol for phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate in KCNQ1 channel regulation.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 28;9(3):e93255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093255. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24681627 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac purinergic signalling in health and disease.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Mar;11(1):1-46. doi: 10.1007/s11302-014-9436-1. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 25527177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCNE1 enhances phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) sensitivity of IKs to modulate channel activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 31;108(22):9095-100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100872108. Epub 2011 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21576493 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanisms underlying the modulation of GIRK1/GIRK4 heteromeric channels by P2Y receptors.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Apr;463(4):625-33. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1082-2. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 22362083
References
-
- BELARDINELLI L., ISENBERG G. Isolated atrial myocytes: adenosine and acetylcholine increase potassium conductance. Am. J. Physiol. 1983;244:H734–H737. - PubMed
-
- BENDER K., WELLNER-KIENITZ M.-C., POTT L. Transfection of a phosphatidyl-4-phosphate 5-kinase gene into rat atrial myocytes removes inhibition of GIRK current by endothelin and α-adrenergic agonists. FEBS Lett. 2002;529:356–360. - PubMed
-
- BIAN J., CUI J., MCDONALD T.V. HERG K+ channel activity is regulated by changes in phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Circ. Res. 2001;89:1168–1176. - PubMed
-
- BRAUN A.P., FEDIDA D., GILES W.R. Activation of α1-aderenoceptors modulates the inwardly rectifying potassium currents of mammalian atrial myocytes. Pflügers Arch. 1992;421:431–439. - PubMed
-
- BREITWIESER G.E., SZABO G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and β-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985;317:538–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

