Vaccinia virus protein A46R targets multiple Toll-like-interleukin-1 receptor adaptors and contributes to virulence
- PMID: 15767367
- PMCID: PMC2213104
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041442
Vaccinia virus protein A46R targets multiple Toll-like-interleukin-1 receptor adaptors and contributes to virulence
Abstract
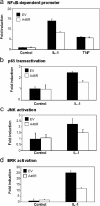
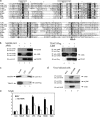
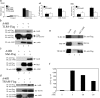
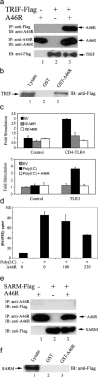
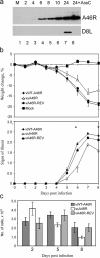
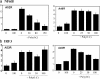
Viral immune evasion strategies target key aspects of the host antiviral response. Recently, it has been recognized that Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have a role in innate defense against viruses. Here, we define the function of the vaccinia virus (VV) protein A46R and show it inhibits intracellular signalling by a range of TLRs. TLR signalling is triggered by homotypic interactions between the Toll-like-interleukin-1 resistance (TIR) domains of the receptors and adaptor molecules. A46R contains a TIR domain and is the only viral TIR domain-containing protein identified to date. We demonstrate that A46R targets the host TIR adaptors myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), MyD88 adaptor-like, TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta (TRIF), and the TRIF-related adaptor molecule and thereby interferes with downstream activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappaB. TRIF mediates activation of interferon (IFN) regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and induction of IFN-beta by TLR3 and TLR4 and suppresses VV replication in macrophages. Here, A46R disrupted TRIF-induced IRF3 activation and induction of the TRIF-dependent gene regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted. Furthermore, we show that A46R is functionally distinct from another described VV TLR inhibitor, A52R. Importantly, VV lacking the A46R gene was attenuated in a murine intranasal model, demonstrating the importance of A46R for VV virulence.
Figures
References
-
- Janeway, C.A. Jr., and R. Medzhitov. 2002. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Takeda, K., T. Kaisho, and S. Akira. 2003. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Dunne, A., and L.A.J. O'Neill. 2003. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci. STKE. 2003:re3. - PubMed
-
- Zhang, D., G. Zhang, M.S. Hayden, M.B. Greenblatt, C. Bussey, R.A. Flavell, and S. Ghosh. 2004. A toll-like receptor that prevents infection by uropathogenic bacteria. Science. 303:1522–1526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

