Control of VP16 translation by the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP27
- PMID: 15767413
- PMCID: PMC1061579
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4120-4131.2005
Control of VP16 translation by the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP27
Abstract
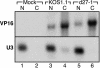
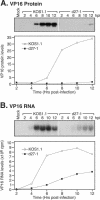
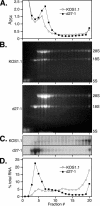
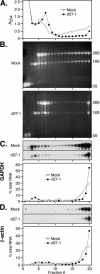
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) ICP27 is an essential and multifunctional regulator of gene expression that modulates the synthesis and maturation of viral and cellular mRNAs. Processes that are affected by ICP27 include transcription, pre-mRNA splicing, polyadenylation, and nuclear RNA export. We have examined how ICP27 influences the expression of the essential HSV tegument protein and transactivator of immediate-early gene expression VP16. We monitored the effects of ICP27 on the levels, nuclear export, and polyribosomal association of VP16 mRNA and on the amount and stability of VP16 protein. Deletion of ICP27 reduced the levels of VP16 mRNA without altering its nuclear export or the stability of the encoded protein. However, the translational yield of the VP16 mRNA produced in the absence of ICP27 was reduced 9- to 80-fold relative to that for wild-type infection, suggesting a defect in translation. In the absence of ICP27, the majority of cytoplasmic VP16 mRNA was not associated with actively translating polyribosomes but instead cosedimented with 40S ribosomal subunits, indicating that the translational defect is likely at the level of initiation. These effects were mRNA specific, as polyribosomal analysis of two cellular transcripts (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and beta-actin) and two early HSV transcripts (thymidine kinase and ICP8) indicated that ICP27 is not required for efficient translation of these mRNAs. Thus, we have uncovered a novel mRNA-specific translational regulatory function of ICP27.
Figures


References
-
- Chou, J., J. J. Chen, M. Gross, and B. Roizman 1995. Association of a Mr 90,000 phosphoprotein with protein kinase PKR in cells exhibiting enhanced phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF-2α and premature shutoff of protein synthesis after infection with γ134.5− mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:10516-10520. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

