Activation of CREB/ATF sites by polyomavirus large T antigen
- PMID: 15767419
- PMCID: PMC1061560
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4180-4190.2005
Activation of CREB/ATF sites by polyomavirus large T antigen
Abstract
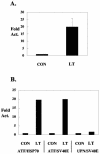
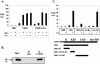
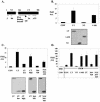
Polyomavirus large T antigen (LT) has a direct role in viral replication and a profound effect on cell phenotype. It promotes cell cycle progression, immortalizes primary cells, blocks differentiation, and causes apoptosis. While much of large T function is related to its effects on tumor suppressors of the retinoblastoma susceptibility (Rb) gene family, we have previously shown that activation of the cyclin A promoter can occur through a non-Rb-dependent mechanism. Here we show that activation occurs via an ATF/CREB site. Investigation of the mechanism indicates that large T can synergize with CREB family members to activate transcription. Experiments with Gal4-CREB constructs show that synergy is independent of CREB phosphorylation by protein kinase A. Examination of synergy with Gal4-CREB deletion constructs indicates that large T acts on the constitutive activation domain of CREB. Large T can bind to CREB in vivo. Genetic analysis shows that the DNA-binding domain (residues 264 to 420) is sufficient to activate transcription when it is localized to the nucleus. Further analysis of the DNA-binding domain shows that while site-specific DNA binding is not required, non-site-specific DNA binding is important for the activation. Thus, CREB binding and DNA binding are both important for large T activation of CREB/ATF sites. In contrast to previous models where large T transactivation occurred indirectly, these results also suggest that large T can act directly at promoters to activate transcription.
Figures


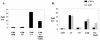

Similar articles
-
CREB/ATF-dependent repression of cyclin a by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein.J Virol. 2001 Mar;75(5):2161-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.5.2161-2173.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160720 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of transactivation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 promoter: Binding of Tax to Tax-responsive element 1 is mediated by the cyclic AMP-responsive members of the CREB/ATF family of transcription factors.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2174-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.5.2174. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8628284 Free PMC article.
-
An ATF/CREB binding motif is required for aberrant constitutive expression of the MHC class II DR alpha promoter and activation by SV40 T-antigen.Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4881-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4881. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992. PMID: 1329030 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ATF/CREB family members in cell growth, survival and apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2003 Jun;8(3):225-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1023633704132. Apoptosis. 2003. PMID: 12766482 Review.
-
Regulation of Hepatic Metabolism and Cell Growth by the ATF/CREB Family of Transcription Factors.Diabetes. 2021 Mar;70(3):653-664. doi: 10.2337/dbi20-0006. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33608424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human SNF2L gene is regulated constitutively and inducibly in neural cells via a cAMP-response element.Yonsei Med J. 2013 May 1;54(3):772-7. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.772. Yonsei Med J. 2013. PMID: 23549828 Free PMC article.
-
Viral drug sensitivity testing using quantitative PCR: effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on polyomavirus BK replication.Am J Clin Pathol. 2010 Dec;134(6):916-20. doi: 10.1309/AJCP7JYHJN1PGQVC. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010. PMID: 21088155 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Transcriptional Activity of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Large T-Antigen by PKA-Mediated Phosphorylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):895. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010895. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614338 Free PMC article.
-
Viral interference with DNA repair by targeting of the single-stranded DNA binding protein RPA.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Oct;9(10):e1003725. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003725. Epub 2013 Oct 24. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24204272 Free PMC article.
-
Polyomavirus large T antigen binds symmetrical repeats at the viral origin in an asymmetrical manner.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13751-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01740-13. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24109229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, and K. Struhl. 1992. Short protocols in molecular biology, 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
-
- Basilico, C., D. Zouzias, G. Della Valle, S. Gattoni, V. Colantuoni, R. Fenton, and L. Dailey. 1980. Integration and excision of polyoma virus genomes. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 44:611-620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

