Silencing of integrated human papillomavirus type 18 oncogene transcription in cells expressing SerpinB2
- PMID: 15767426
- PMCID: PMC1061571
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4246-4256.2005
Silencing of integrated human papillomavirus type 18 oncogene transcription in cells expressing SerpinB2
Abstract
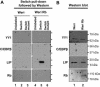
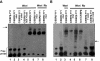
The serine protease inhibitor SerpinB2 (PAI-2), a major product of differentiating squamous epithelial cells, has recently been shown to bind and protect the retinoblastoma protein (Rb) from degradation. In human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV-18)-transformed epithelial cells the expression of the E6 and E7 oncoproteins is controlled by the HPV-18 upstream regulatory region (URR). Here we illustrate that PAI-2 expression in the HPV-18-transformed cervical carcinoma line HeLa resulted in the restoration of Rb expression, which led to the functional silencing of transcription from the HPV-18 URR. This caused loss of E7 protein expression and restoration of multiple E6- and E7-targeted host proteins, including p53, c-Myc, and c-Jun. Rb expression emerged as sufficient for the transcriptional repression of the URR, with repression mediated via the C/EBPbeta-YY1 binding site (URR 7709 to 7719). In contrast to HeLa cells, where the C/EBPbeta-YY1 dimer binds this site, in PAI-2- and/or Rb-expressing cells the site was occupied by the dominant-negative C/EBPbeta isoform liver-enriched transcriptional inhibitory protein (LIP). PAI-2 expression thus has a potent suppressive effect on HPV-18 oncogene transcription mediated by Rb and LIP, a finding with potential implications for prognosis and treatment of HPV-transformed lesions.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Suppression of tumorigenesis by transcription units expressing the antisense E6 and E7 messenger RNA (mRNA) for the transforming proteins of the human papilloma virus and the sense mRNA for the retinoblastoma gene in cervical carcinoma cells.Cancer Gene Ther. 1995 Mar;2(1):19-32. Cancer Gene Ther. 1995. PMID: 7621252
-
Overexpression of C/EBPbeta represses human papillomavirus type 18 upstream regulatory region activity in HeLa cells by interfering with the binding of TATA-binding protein.J Virol. 1998 Mar;72(3):2113-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.3.2113-2124.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9499067 Free PMC article.
-
The role of HPV oncoproteins and cellular factors in maintenance of hTERT expression in cervical carcinoma cells.Gynecol Oncol. 2004 Jul;94(1):40-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.03.041. Gynecol Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15262117
-
Interactions of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with tumour suppressor gene products.Cancer Surv. 1992;12:197-217. Cancer Surv. 1992. PMID: 1322242 Review.
-
Cellular targets of the oncoproteins encoded by the cancer associated human papillomaviruses.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991;22:239-48. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991. PMID: 1668886 Review.
References
-
- Antalis, T. M., M. La Linn, K. Donnan, L. Mateo, J. Gardner, J. L. Dickinson, K. Buttigieg, and A. Suhrbier. 1998. The serine proteinase inhibitor (serpin) plasminogen activation inhibitor type 2 protects against viral cytopathic effects by constitutive interferon alpha/beta priming. J. Exp. Med. 187:1799-1811. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badal, S., V. Badal, I. E. Calleja-Macias, M. Kalantari, L. S. Chuang, B. F. Li, and H. U. Bernard. 2004. The human papillomavirus-18 genome is efficiently targeted by cellular DNA methylation. Virology 324:483-492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

