The Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP protein preferentially coactivates EBNA2-mediated stimulation of latent membrane proteins expressed from the viral divergent promoter
- PMID: 15767449
- PMCID: PMC1061541
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4492-4505.2005
The Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP protein preferentially coactivates EBNA2-mediated stimulation of latent membrane proteins expressed from the viral divergent promoter
Abstract
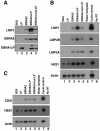
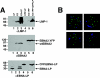
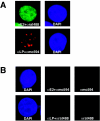
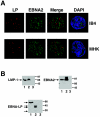
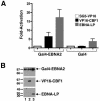
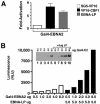
The mechanistic contribution of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) EBNA-LP protein to B-cell immortalization remains an enigma. However, previous studies have indicated that EBNA-LP may contribute to immortalization by enhancing EBNA2-mediated transcriptional activation of the LMP-1 gene. To gain further insight into the potential role EBNA-LP has in EBV-mediated B-cell immortalization, we asked whether it is a global or gene-specific coactivator of EBNA2 and whether coactivation requires interaction between these proteins. In type I Burkitt's lymphoma cells, we found that EBNA-LP strongly coactivated EBNA2 stimulation of LMP-1 and LMP2B RNAs, which are expressed from the viral divergent promoter. Surprisingly, the viral LMP2A gene and cellular CD21 and Hes-1 genes were induced by EBNA2 but showed no further induction after EBNA-LP coexpression. We also found that EBNA-LP did not stably interact with EBNA2 in coimmunoprecipitation assays, even though the conditions were adequate to observe specific interactions between EBNA2 and its cellular cofactor, CBF1. Colocalization between EBNA2 and EBNA-LP was not detectable in EBV-transformed cell lines or transfected type I Burkitt's cells. Finally, no significant interactions between EBNA2 and EBNA-LP were found with mammalian two-hybrid assays. From this data, we conclude that EBNA-LP is not a global coactivator of EBNA2 targets, but it preferentially coactivates EBNA2 stimulation of the viral divergent promoter. While this may require specific transient interactions between these proteins that only occur in the context of the divergent promoter, our data strongly suggest that EBNA-LP also cooperates with EBNA2 through mechanisms that do not require direct or indirect complex formation between these proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The NP9 protein encoded by the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K(HML-2) negatively regulates gene activation of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2).Int J Cancer. 2011 Sep 1;129(5):1105-15. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25760. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21710493
-
EBNA2 and Its Coactivator EBNA-LP.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:35-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428371 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-LP is essential for transforming naïve B cells, and facilitates recruitment of transcription factors to the viral genome.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Feb 20;14(2):e1006890. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006890. eCollection 2018 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29462212 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of the Epstein-Barr virus-coded leader protein EBNA-LP as a co-activator of EBNA2 function.J Gen Virol. 2001 Dec;82(Pt 12):3067-3079. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-82-12-3067. J Gen Virol. 2001. PMID: 11714985
-
Cytokine mediated induction of the major Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded transforming protein, LMP-1.Immunol Lett. 2006 Apr 15;104(1-2):83-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16386314 Review.
Cited by
-
Truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus protein EBNA-LP protects against caspase-dependent apoptosis by inhibiting protein phosphatase 2A.J Virol. 2007 Jul;81(14):7598-607. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02435-06. Epub 2007 May 9. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17494066 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen leader protein localizes to promoters and enhancers with cell transcription factors and EBNA2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 12;110(46):18537-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317608110. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24167291 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of importin-α bound to the nuclear localization signal of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP protein.Protein Sci. 2017 Jun;26(6):1231-1235. doi: 10.1002/pro.3173. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28383161 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Herpesvirus Infection and Host Defense by PML Nuclear Bodies.Viruses. 2009 Dec;1(3):1240-64. doi: 10.3390/v1031240. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Viruses. 2009. PMID: 21994592 Free PMC article.
-
B cells infected with Type 2 Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) have increased NFATc1/NFATc2 activity and enhanced lytic gene expression in comparison to Type 1 EBV infection.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Feb 14;16(2):e1008365. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008365. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32059024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan, G. J., G. J. Inman, B. D. Parker, D. T. Rowe, and P. J. Farrell. 1992. Cell growth effects of Epstein-Barr virus leader protein. J. Gen. Virol. 73:1547-1551. - PubMed
-
- Allday, M. J., D. H. Crawford, and J. A. Thomas. 1993. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 6 induces expression of the EBV latent membrane protein and an activated phenotype in Raji cells. J. Gen. Virol. 74:361-369. - PubMed
-
- Castillo, J. P., and T. F. Kowalik. 2002. Human cytomegalovirus immediate early proteins and cell growth control. Gene 290:19-34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

