The AAA+ protein torsinA interacts with a conserved domain present in LAP1 and a novel ER protein
- PMID: 15767459
- PMCID: PMC2171781
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200411026
The AAA+ protein torsinA interacts with a conserved domain present in LAP1 and a novel ER protein
Abstract
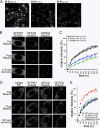
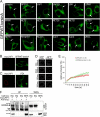
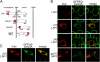
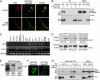
A glutamic acid deletion (DeltaE) in the AAA+ protein torsinA causes DYT1 dystonia. Although the majority of torsinA resides within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), torsinA binds a substrate in the lumen of the nuclear envelope (NE), and the DeltaE mutation enhances this interaction. Using a novel cell-based screen, we identify lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1) as a torsinA-interacting protein. LAP1 may be a torsinA substrate, as expression of the isolated lumenal domain of LAP1 inhibits the NE localization of "substrate trap" EQ-torsinA and EQ-torsinA coimmunoprecipitates with LAP1 to a greater extent than wild-type torsinA. Furthermore, we identify a novel transmembrane protein, lumenal domain like LAP1 (LULL1), which also appears to interact with torsinA. Interestingly, LULL1 resides in the main ER. Consequently, torsinA interacts directly or indirectly with a novel class of transmembrane proteins that are localized in different subdomains of the ER system, either or both of which may play a role in the pathogenesis of DYT1 dystonia.
Figures

References
-
- Berardelli, A., J.C. Rothwell, M. Hallett, P.D. Thompson, M. Manfredi, and C.D. Marsden. 1998. The pathophysiology of primary dystonia. Brain. 121:1195–1212. - PubMed
-
- Burke, B., and C.L. Stewart. 2002. Life at the edge: the nuclear envelope and human disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:575–585. - PubMed
-
- De Sandre-Giovannoli, A., R. Bernard, P. Cau, C. Navarro, J. Amiel, I. Boccaccio, S. Lyonnet, C.L. Stewart, A. Munnich, M. Le Merrer, and N. Levy. 2003. Lamin a truncation in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria. Science. 300:2055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

