The polyglutamine neurodegenerative protein ataxin 3 regulates aggresome formation
- PMID: 15767577
- PMCID: PMC555481
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407252102
The polyglutamine neurodegenerative protein ataxin 3 regulates aggresome formation
Abstract
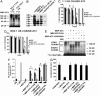
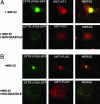
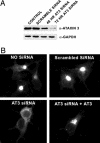
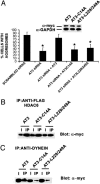
The polyglutamine-containing neurodegenerative protein ataxin 3 (AT3) has deubiquitylating activity and binds ubiquitin chains with a preference for chains of four or more ubiquitins. Here we characterize the deubiquitylating activity of AT3 in vitro and show it trims/edits K48-linked ubiquitin chains. AT3 also edits polyubiquitylated (125)I-lysozyme and decreases its degradation by proteasomes. Cellular studies show that endogenous AT3 colocalizes with aggresomes and preaggresome particles of the misfolded cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) mutant CFTRDeltaF508 and associates with histone deacetylase 6 and dynein, proteins required for aggresome formation and transport of misfolded protein. Small interfering RNA knockdown of AT3 greatly reduces aggresomes formed by CFTRDeltaF508, demonstrating a critical role of AT3 in this process. Wild-type AT3 restores aggresome formation; however, AT3 with mutations in the active site or ubiquitin interacting motifs cannot restore aggresome formation in AT3 knockdown cells. These same mutations decrease the association of AT3 and dynein. These data indicate that the deubiquitylating activity of AT3 and its ubiquitin interacting motifs as well play essential roles in CFTRDeltaF508 aggresome formation.
Figures

References
-
- Takiyama, Y., Nishizawa, M., Tanaka, H., Kawashima, S., Sakamoto, H., Karube, Y., Shimazaki, H., Soutome, M., Endo, K., Ohta, S., et al. (1993) Nat. Genet. 4, 300–304. - PubMed
-
- Paulson, H. L., Perez, M. K., Trottier, Y., Trojanowski, J. Q., Subramony, S. H., Das, S. S., Vig, P., Mandel, J. L., Fischbeck, K. H. & Pittman, R. N. (1997) Neuron 19, 333–344. - PubMed
-
- DiFiglia, M., Sapp, E., Chase, K. O., Davies, S. W., Bates, G. P., Vonsattel, J. P. & Aronin, N. (1997) Science 277, 1990–1993. - PubMed
-
- Skinner, P. J., Koshy, B. T., Cummings, C. J., Klement, I. A., Helin, K., Servadio, A., Zoghbi, H. Y. & Orr, H. T. (1997) Nature 389, 971–974. - PubMed
-
- Li, M., Miwa, S., Kobayashi, Y., Merry, D. E., Yamamoto, M., Tanaka, F., Doyu, M., Hashizume, Y., Fischbeck, K. H., et al. (1998) Ann. Neurol. 44, 249–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

