Relationship between histone H3 lysine 9 methylation, transcription repression, and heterochromatin protein 1 recruitment
- PMID: 15767660
- PMCID: PMC1061631
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.7.2525-2538.2005
Relationship between histone H3 lysine 9 methylation, transcription repression, and heterochromatin protein 1 recruitment
Abstract
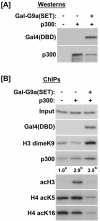
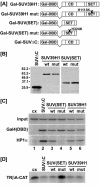
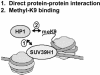
Histone H3 lysine 9 (H3-K9) methylation has been shown to correlate with transcriptional repression and serve as a specific binding site for heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1). In this study, we investigated the relationship between H3-K9 methylation, transcriptional repression, and HP1 recruitment by comparing the effects of tethering two H3-K9-specific histone methyltransferases, SUV39H1 and G9a, to chromatin on transcription and HP1 recruitment. Although both SUV39H1 and G9a induced H3-K9 methylation and repressed transcription, only SUV39H1 was able to recruit HP1 to chromatin. Targeting HP1 to chromatin required not only K9 methylation but also a direct protein-protein interaction between SUV39H1 and HP1. Targeting methyl-K9 or a HP1-interacting region of SUV39H1 alone to chromatin was not sufficient to recruit HP1. We also demonstrate that methyl-K9 can suppress transcription independently of HP1 through a mechanism involving histone deacetylation. In an effort to understand how H3-K9 methylation led to histone deacetylation in both H3 and H4, we found that H3-K9 methylation inhibited histone acetylation by p300 but not its association with chromatin. Collectively, these data indicate that H3-K9 methylation alone can suppress transcription but is insufficient for HP1 recruitment in the context of chromatin exemplifying the importance of chromatin-associated factors in reading the histone code.
Figures
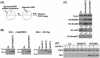




References
-
- Aagaard, L., G. Laible, P. Selenko, M. Schmid, R. Dorn, G. Schotta, S. Kuhfittig, A. Wolf, A. Lebersorger, P. B. Singh, G. Reuter, and T. Jenuwein. 1999. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO J. 18:1923-1938. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almouzni, G., and A. P. Wolffe. 1993. Replication-coupled chromatin assembly is required for the repression of basal transcription in vivo. Genes Dev. 7:2033-2047. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A. J., and T. Kouzarides. 1996. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 384:641-643. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas, R. C. Allshire, and T. Kouzarides. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410:120-124. - PubMed
-
- Chen, D., H. Ma, H. Hong, S. S. Koh, S. M. Huang, B. T. Schurter, D. W. Aswad, and M. R. Stallcup. 1999. Regulation of transcription by a protein methyltransferase. Science 284:2174-2177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
