Distinct signaling events downstream of mTOR cooperate to mediate the effects of amino acids and insulin on initiation factor 4E-binding proteins
- PMID: 15767663
- PMCID: PMC1061630
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.7.2558-2572.2005
Distinct signaling events downstream of mTOR cooperate to mediate the effects of amino acids and insulin on initiation factor 4E-binding proteins
Abstract
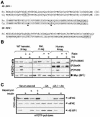
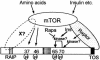
Signaling through the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) controls cell size and growth as well as other functions, and it is a potential therapeutic target for graft rejection, certain cancers, and disorders characterized by inappropriate cell or tissue growth. mTOR signaling is positively regulated by hormones or growth factors and amino acids. mTOR signaling regulates the phosphorylation of several proteins, the best characterized being ones that control mRNA translation. Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) undergoes phosphorylation at multiple sites. Here we show that amino acids regulate the N-terminal phosphorylation sites in 4E-BP1 through the RAIP motif in a rapamycin-insensitive manner. Several criteria indicate this reflects a rapamycin-insensitive output from mTOR. In contrast, the insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of the C-terminal site Ser64/65 is generally sensitive to rapamycin, as is phosphorylation of another well-characterized target for mTOR signaling, S6K1. Our data imply that it is unlikely that mTOR directly phosphorylates Thr69/70 in 4E-BP1. Although 4E-BP1 and S6K1 bind the mTOR partner, raptor, our data indicate that the outputs from mTOR to 4E-BP1 and S6K1 are distinct. In cells, efficient phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 requires it to be able to bind to eIF4E, whereas phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by mTOR in vitro shows no such preference. These data have important implications for understanding signaling downstream of mTOR and the development of new strategies to impair mTOR signaling.
Figures





References
-
- Avruch, J., C. Belham, Q. Weng, K. Hara, and K. Yonezawa. 2001. The p70 S6 kinase integrates nutrient and growth signals to control translational capacity. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 26:115-154. - PubMed
-
- Beugnet, A., X. Wang, and C. G. Proud. 2003. The TOR-signaling and RAIP motifs play distinct roles in the mTOR-dependent phosphorylation of initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 278:40722. - PubMed
-
- Brunn, G. J., C. C. Hudson, A. Sekulic, J. M. Williams, H. Hosoi, P. J. Houghton, J. C. Lawrence, and R. T. Abraham. 1997. Phosphorylation of the translational repressor PHAS-I by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Science 277:99-101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
