Deregulated E2F activity induces hyperplasia and senescence-like features in the mouse pituitary gland
- PMID: 15767672
- PMCID: PMC1061636
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.7.2660-2672.2005
Deregulated E2F activity induces hyperplasia and senescence-like features in the mouse pituitary gland
Abstract
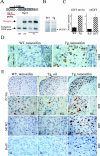
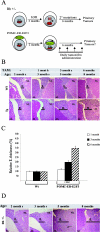
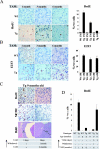
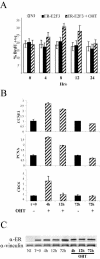
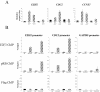
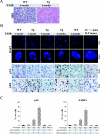
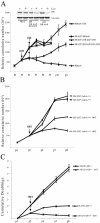
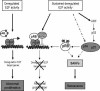
The retinoblastoma gene, RB1, is one of the most frequently mutated genes in human cancer. Rb heterozygous mice develop pituitary tumors with 100% incidence, and the E2F transcription factors are required for this. To assess whether deregulated E2F activity is sufficient to induce pituitary tumors, we generated transgenic mice expressing an inducible E2F3 protein in the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland. We found that short-term deregulation of E2F activity, similar to the earliest stages of Rb loss, is able to induce abnormal proliferation of otherwise quiescent melanotrophs. However, while long-term exposure to deregulated E2F activity results in hyperplasia of the intermediate lobe, it did not lead to tumor formation. In fact, melanotrophs become insensitive to sustained E2F stimulation and enter an irreversible senescence-like state. Thus, although deregulated E2F activity results in hyperproliferation, it is not sufficient to mimic loss of Rb, sustain proliferation of melanotrophs, and ultimately induce pituitary tumors. Similarly, we found that primary cells in tissue culture become insensitive to sustained E2F3 activation and undergo premature senescence in a pRB-, p16Ink4a-, and p19Arf-dependent manner. Thus, we conclude that deregulated E2F activity is not sufficient to fully mimic loss of Rb due to the engagement of a senescence response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural precursor cells differentiating in the absence of Rb exhibit delayed terminal mitosis and deregulated E2F 1 and 3 activity.Dev Biol. 1999 Mar 15;207(2):257-70. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9162. Dev Biol. 1999. PMID: 10068462
-
The E2F-family proteins induce distinct cell cycle regulatory factors in p16-arrested, U343 astrocytoma cells.Oncogene. 1998 Aug 20;17(7):867-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202008. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9780003
-
C/EBPbeta cooperates with RB:E2F to implement Ras(V12)-induced cellular senescence.EMBO J. 2005 Sep 21;24(18):3301-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600789. Epub 2005 Aug 18. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 16107878 Free PMC article.
-
Rb/E2F: a two-edged sword in the melanocytic system.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005 Jun;24(2):339-56. doi: 10.1007/s10555-005-1582-z. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005. PMID: 15986142 Review.
-
Activity of the retinoblastoma family proteins, pRB, p107, and p130, during cellular proliferation and differentiation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jun;31(3):237-71. doi: 10.3109/10409239609106585. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8817077 Review.
Cited by
-
A new p53 target gene, RKIP, is essential for DNA damage-induced cellular senescence and suppression of ERK activation.Neoplasia. 2013 Jul;15(7):727-37. doi: 10.1593/neo.121862. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23814485 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic nature of senescence in cancer.Nat Cell Biol. 2019 Jan;21(1):94-101. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0249-2. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30602768 Review.
-
Cell Cycle Regulators and Lineage-Specific Therapeutic Targets for Cushing Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Aug 10;9:444. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00444. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30147673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Mechanisms of Plant-Derived Compounds Targeting Brain Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 30;19(2):395. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020395. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29385679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accumulation of senescent cells in mitotic tissue of aging primates.Mech Ageing Dev. 2007 Jan;128(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2006.11.008. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007. PMID: 17116315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brehm, A., and T. Kouzarides. 1999. Retinoblastoma protein meets chromatin. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24:142-145. - PubMed
-
- Clarke, A., E. Maandag, M. van Roon, N. van der Lugt, M. van der Valk, M. Hooper, A. Berns, and H. te Riele. 1992. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature 359:328-330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
